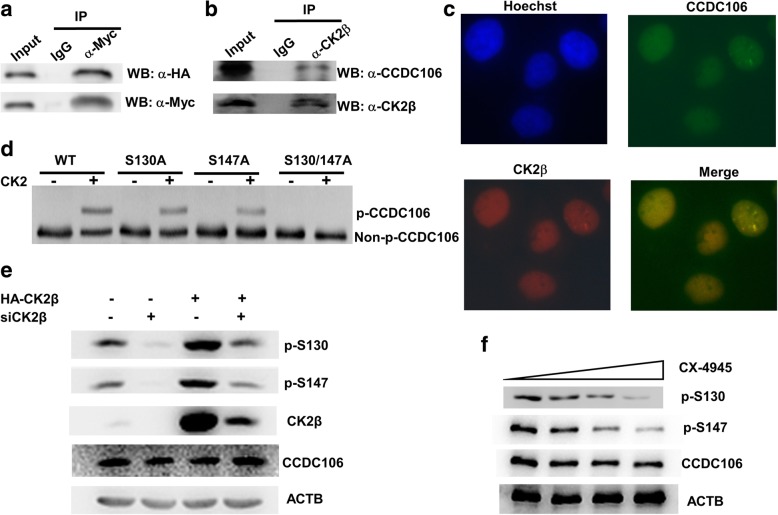
Fig. 2.
CK2 interacts with and phosphorylates CCDC106. a and b The interaction between CK2β and p53 was investigated by a Co-IP assay. Lysates were isolated from Hek293 cells cotransfected with HA-p53 and Myc-CCDC106 (a) and HeLa cells (b) were precipitated with control IgG or the indicated antibody. The immune complexes were subjected to WB. c Immunofluorescence staining of HeLa cells. A murine anti-CK2β monoclonal antibody and a Texas Red-conjugated anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (red) were used to analyze CK2β, whereas a rabbit anti-CCDC106 polyclonal antibody and a FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (green) were used to analyze CCDC106. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). The yellow color in the merged image represents the colocalization of CK2β and the CCDC106 protein. d Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and WB analysis. The bacterially expressed and purified GST-fusion proteins were incubated with CK2 holoenzyme for 1 h. Then, the reaction mixture was separated by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and subjected to WB using anti-GST antibody. e and f The influence of CK2β expression (e) and CX-4945 treatment (f) on the phosphorylation of the CCDC106 protein. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA (siCK2β) and/or the expression plasmid (HA-CK2β) of CK2β (e) or treated with increasing concentrations of CX-4945 (f). At 24 h after transfection or treatment, phosphorylation of CCDC106 was analyzed by phospho-CCDC106 (p-S130) and phospho-CCDC106 (p-S147) antibodies