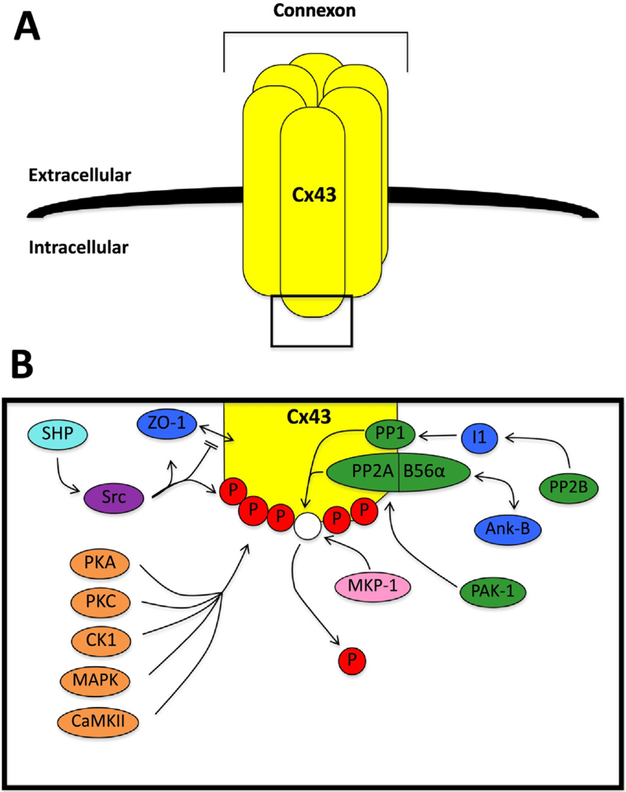
Fig. 1.
Connexin 43 phosphorylation overview. A. An overview of a connexon formed from connexin 43 (Cx43). B. A schematic of the interactions between Cx43 and key kinases and phosphatases. Shown are: a) serine/threonine kinases (orange), including protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC), casein kinase 1 (CK1), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII); b) serine/threonine phosphatases (green), including protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), calcineurin (PP2B), and p-21 activated kinase-1 (PAK-1); c) the tyrosine kinase (purple) Src kinase (Src); d) the tyrosine phosphatase (light blue) Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP); e) the dual specificity phosphatase (pink) mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1); and f) related proteins (dark blue) including zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), inhibitor 1 (I1), and ankyrin-B (Ank-B). The phosphate groups are indicated by P. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)