Figure 5.
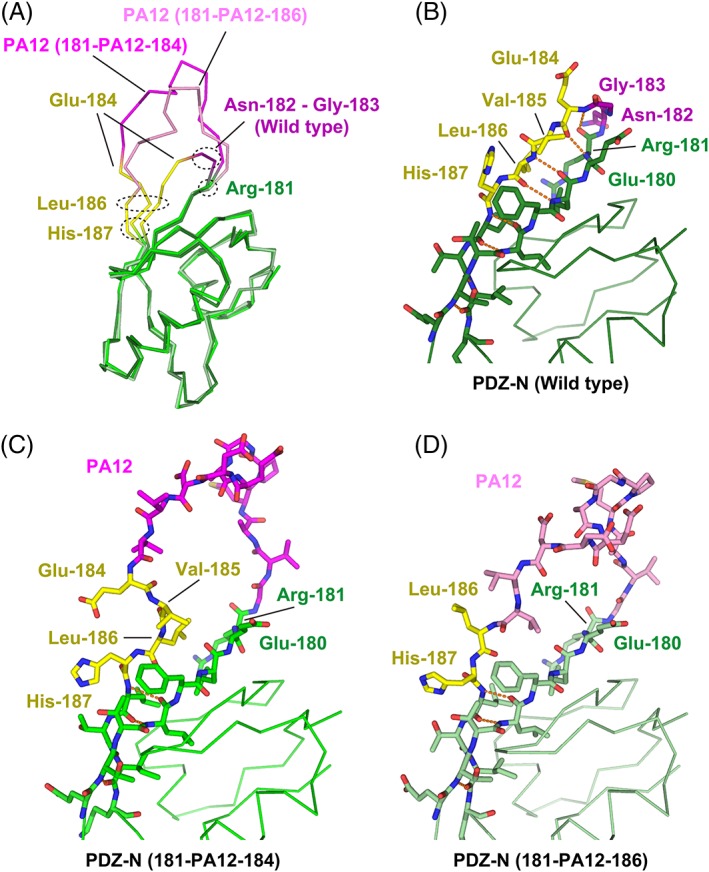
Structural change of the PDZ‐N domain around the PA insertion site. (A) Superposition of the Cα traces. The wild‐type PDZ‐N domain and the two PA‐inserted mutants are displayed as varying shades of the same color scheme. The rigidly‐folded part of the PDZ‐N domain is shown in green where the residues undergoing significant structural changes due to the PA insertion (Glu‐184 to His‐187) are highlighted in yellow. The two residues (Asn‐182 and Gly‐183) deleted to construct the PDZ tandem (181‐PA12‐184) are shown in dark magenta. The PA12 residues of PDZ tandem (181‐PA12‐184) and (181‐PA12‐186) are shown in bright magenta and light magenta, respectively. Close‐up view of the PA insertion site of the wild type PDZ‐N domain (B), PDZ tandem (181‐PA12‐184) (C), and PDZ tandem (181‐PA12‐186) (D). Inter‐strand hydrogen bonds are shown as orange dotted lines.
