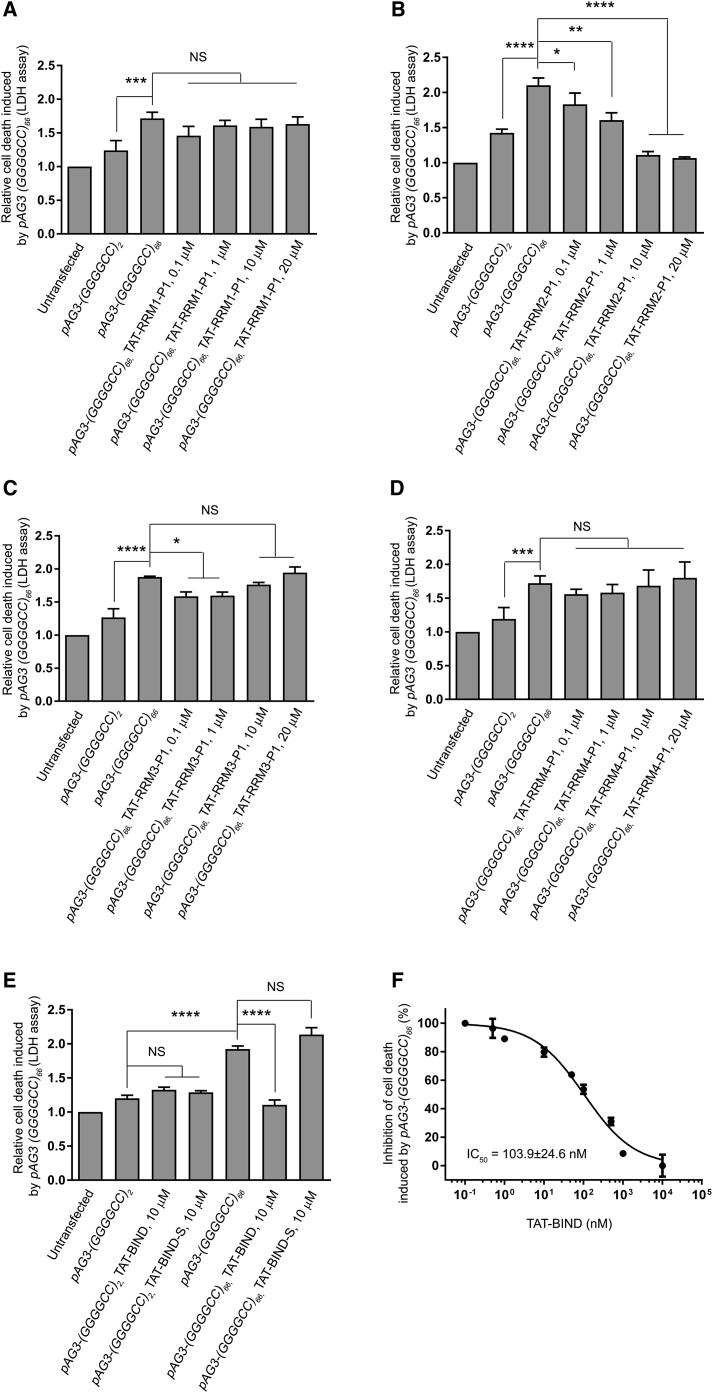
Figure 1.
TAT-RRM2-P1 (TAT-BIND) Significantly Suppressed Cell Death Induced by pAG3-(GGGGCC)66 in SK-N-MC Cells
(A) TAT-RRM1-P1 treatment did not alter pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death. (B) TAT-RRM2-P1 suppressed pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Low concentrations, but not high concentrations, of TAT-RRM3-P1 slightly suppressed pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death. (D) TAT-RRM4-P1 treatment did not alter pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death. 1 μg pAg3-(GGGGCC)2/66 plasmid was used to transfect SK-N-MC cells, followed by application of the respective TAT peptides (0.1, 1, 10, and 20 μM). LDH enzyme activity in the cell culture medium was measured 48 h after treatment. The results of the experimental groups were normalized to the untransfected controls. (E) Application of TAT-BIND or the scrambled control TAT-BIND-S didn’t elicit any observable cytotoxicity to pAG3-(GGGGCC)2/66-expressing cells. TAT-BIND, but not TAT-BIND-S, could suppress pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death. (F) Half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) of TAT-BIND on the inhibition of pAG3-(GGGGCC)66-induced cell death. The IC50 value represents the concentration of TAT-BIND that decreased LDH enzyme activity by 50% relative to LDH enzyme activity in the untreated control group. The experiments were repeated at least thrice, and data were plotted as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001; NS, no significance.