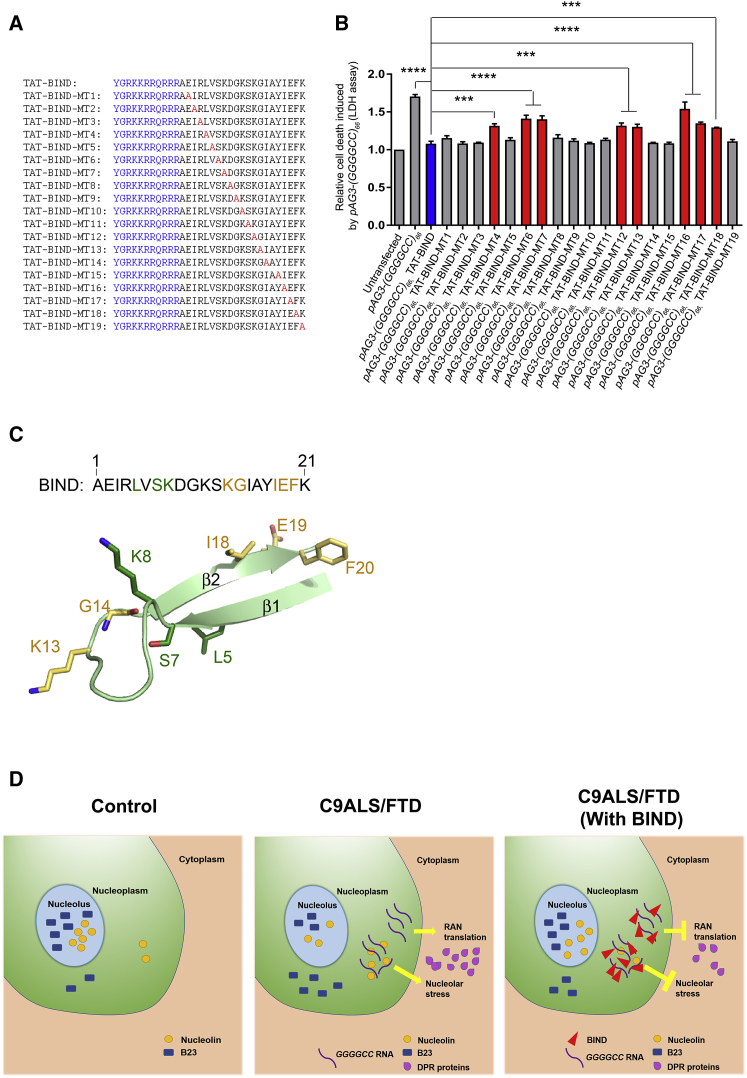
Figure 6.
Calculated IC50 Detection and Structure-Activity Relationship Study of TAT-BIND
(A) Sequences of TAT-BIND mutants. TAT peptide (sequence in bold letters) was attached to the N terminus of each BIND mutant. Alanine substitutions for each mutant have been highlighted in red. (B) Structure-activity relationship studies of TAT-BIND. 1 μg pAg3-(GGGGCC)66 plasmid was used to transfect SK-N-MC cells followed by application of the respective TAT peptides (10 μM). LDH enzyme activity in the cell culture medium was measured 48 h after treatment. (C) Structure of BIND as predicted by PEP-FOLD server.73 Residues that are important for the suppression of both expanded CAG RNA- and expanded GGGGCC RNA-induced cytotoxicity are all located on the same side as strand β2 and colored yellow. Residues crucial for the suppression of expanded GGGGCC RNA-induced cytotoxicity only are colored green. Numbering is based on the amino acid sequence of BIND. (D) Schematic diagram illustrating mechanism of actions of BIND in suppressing neurodegeneration in C9ALS-FTD. The results of the experimental groups were normalized to the untransfected controls. The experiments were repeated at least thrice, and the data were plotted as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001; NS, no significance.