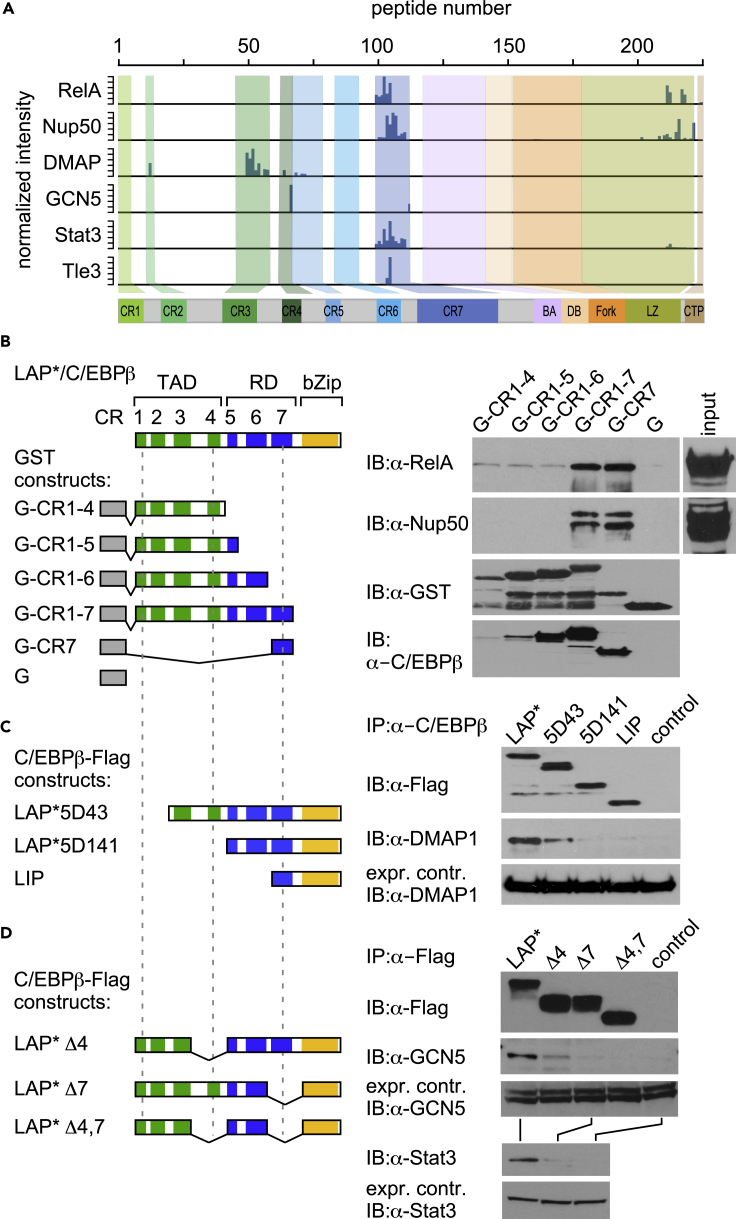
Figure 4.
Validation of Site-Specific Interactions with C/EBPβ
(A) Accumulated binding intensities of interaction partners (indicated on the left) from the PRISMA screen. Bar graphs indicate interactions according to the peptide position in C/EBPβ, as schematically shown underneath.
(B) Top, left: Color-coded scheme of the C/EBPβ protein with dashed lines to aid comparison of constructs shown in (B–D). Top, right: Immunoblots (right) showing interaction of RelA and Nup50/NPAP60L of HEK293T cell lysates with bacterially expressed GST-C/EBPβ constructs. Integrity of GST-C/EBPβ constructs was examined by immunoblotting (as indicated). GST constructs were probed with anti-GST and a polyclonal C/EBPβ antibody that preferentially, but not exclusively, recognizes CR7 as a major epitope. The most intense signals of RelA and Nup50/NPAP60L are associated with the presence of the CR7 region of C/EBPβ. A, antibody; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting.
(C) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged LAP* C/EBPβ or three N-terminal C/EBPβ deletion mutants, followed by immunoblot detection of co-precipitated DMAP1 from HEKT cells.
(D) Immunoprecipitation of HEKT cell expressing LAP* and three different internal deletion mutants of C/EBPβ followed by immunoblot detection of GCN5 and Stat3.