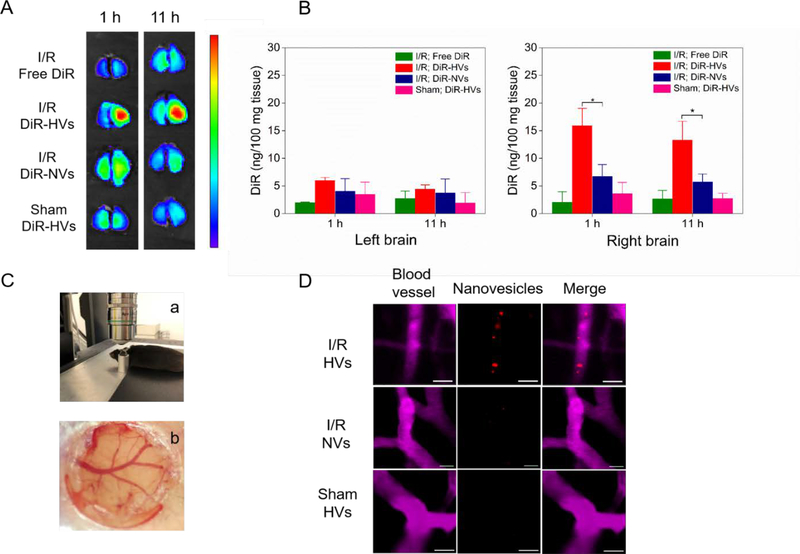
Figure 4.
Binding of nanovesicles to inflamed mouse brain is required for activation of endothelial. (A) Ex vivo brain images at 1 h and 11 h after injection of free DiR, DiR-vesicles (DiR-HVs) or non-differentiated DiR-vesicles (DiR-NVs) in MCAO model, and DiR-HVs in normal mice. (B) Quantification of DiR in the brain tissues in (A) after they were homogenized. All data represent as mean ± SD (n=3). (C) Cranial window is used for live mouse brain imaging. A mouse was placed on a holder during confocal microscopy (a) and a photograph shows cerebral blood vessels under cranial window (b). (D) Real-time confocal images of live mouse brain microcirculation. After MCAO surgery, several Dil labeled-HVs (red) bound to inflamed brain vasculature (top panel), while Dil-NVs were barely observed to bind to inflamed brain vasculature (middle panel). In a healthy mouse (without MCAO surgery), it was not observed that Dil-HVs bound to the brain vasculature (bottom panel). BSA-Cy5 was i.v. administered to label blood vessels (pink). Scale bar=20 μm. Two-sample Student’s t test was performed (*p < 0.05).