Figure 1.
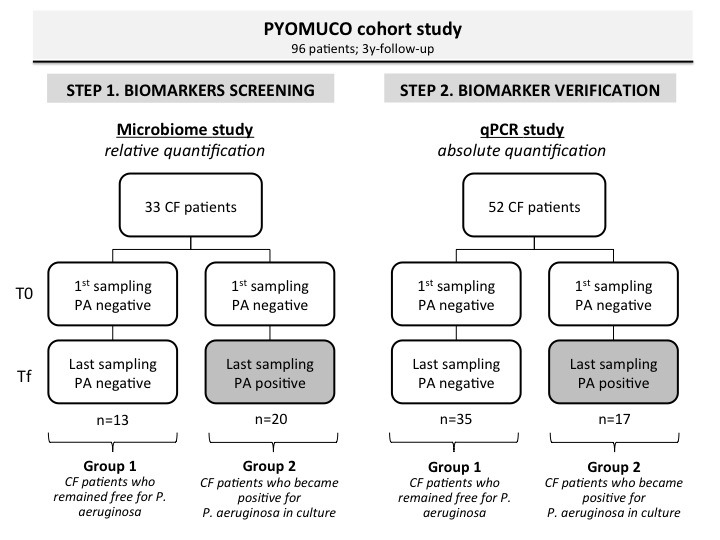
Two-step approach of the study. Samples were issued from the PYOMUCO cohort study whose patients (n=96), initially (T0) all Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) free for at least 1 year, were separated into two groups (group 1 and group 2) according to their P. aeruginosa status at the end of the follow-up (Tf).3 Group 1 patients remained negative, whereas group 2 patients became positive. In a first step carried out in a first set of patients (n=33), bacterial biomarkers associated with P. aeruginosa were screened by 16S-targeted metagenomics; a candidate biomarker (Porphyromonas catoniae) was revealed. In a second step, distribution of the candidate biomarker according to the two groups of patients was verified by quantitative PCR (qPCR) on a second set of patients (n=52) coming from the same cohort. CF, cystic fibrosis.
