Figure 3. Hydrodynamic exosomes isolation in microchips based on various exosome properties.
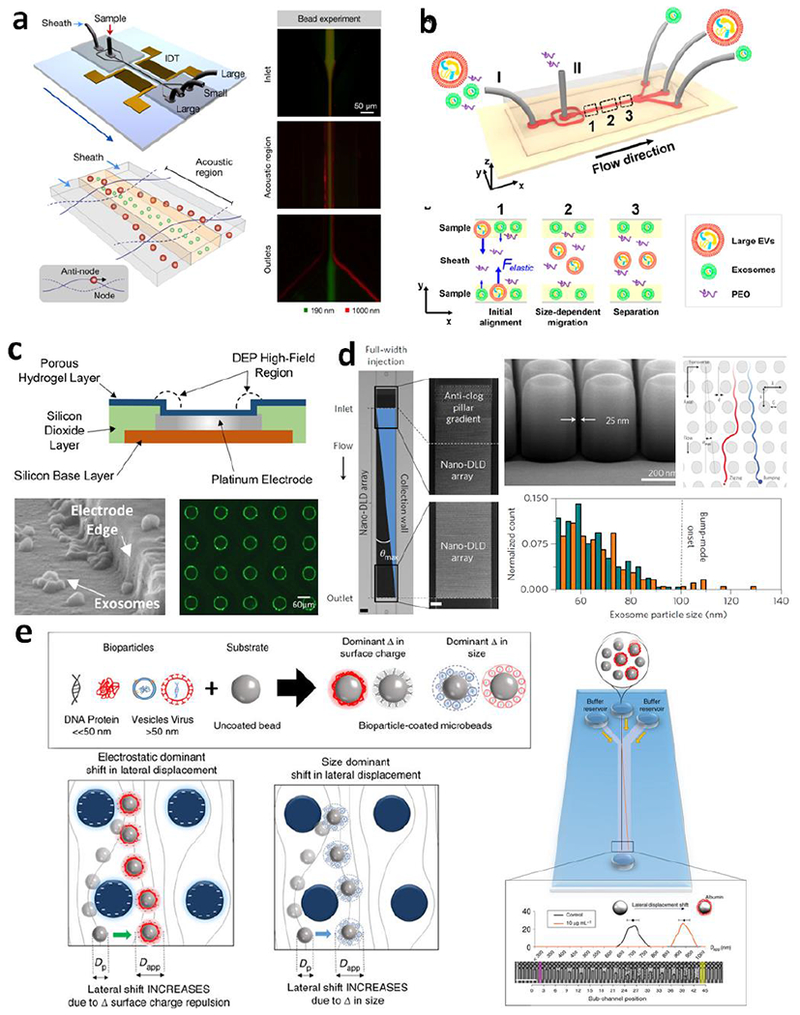
(a) Acoustic nanofilter system for exosomes isolation. Adapted with permission from Ref (103). (b) Isolation of exosomes by microfluidic viscoelastic flows. Adapted with permission from Ref (105). (c) Trapping of exosomes in ACE microarray chip. Adapted with permission from Ref (107). (d) Nano-DLD chips for size sorting of exosomes in laminar flow streams displaced by staggered nanopillars. Adapted with permission from Ref (108). (e) DLD fractionation of bioparticle-bead conjugates in an array of negatively charged micropillars based on the change of size and surface charge of micro-beads upon binding with bioparticles, including proteins and exosomes. Adapted with permission from Ref (109).
