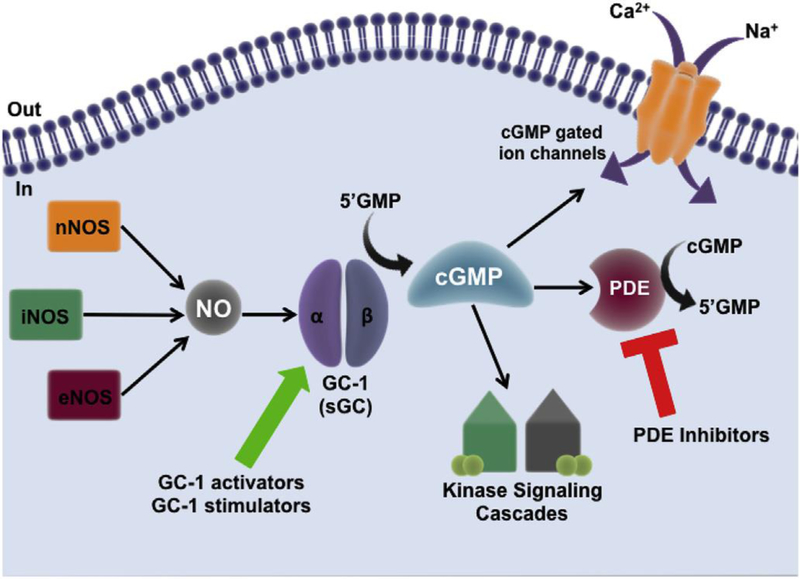
Fig. 2. The NO-GC-1-cGMP pathway.
NO is produced from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) of which there are three isoforms: neuronal NOS1 (nNOS), endothelial NOS3 (eNOS) and inducible NOS2 (iNOS). NO targets guanylate cyclase-1 (GC-1), a heterodimeric protein capable of converting GMP to cGMP. cGMP produced by GC-1 can target cGMP-gated ion channels, and activate downstream kinase signaling cascades. Phosphodiesterase enzymes (PDE) bind to cGMP and catalyse its breakdown into GMP – PDEs act as important regulators of signal transduction mediated by cGMP. cGMP bioavailability in the cell can be modulated in two ways: 1) through the use of GC-1 stimulators and activators, which increase production of cGMP, or, 2) through the use of PDE inhibitors which prevent the breakdown of cGMP in the cell.