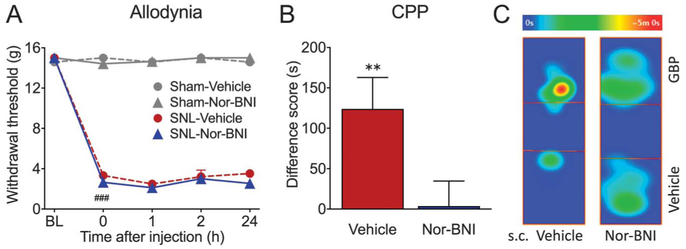
Figure 1.
Systemic nor-BNI relieves aversiveness of ongoing pain but not tactile allodynia in SNL rats. (A) After SNL surgery, rats develop long-lasting mechanical allodynia in the injured paw, demonstrated as reduced tactile paw withdrawal thresholds. Systemic administration of nor-BNI (3 mg/kg, s.c.) or vehicle (saline, s.c.) had no effect on tactile allodynia in either sham or SNL animals during a 24-hour time course. N = 4–8; ###P < 0.001. (B) SNL animals were pretreated with either nor-BNI (3 mg/kg, s.c.) or vehicle (saline, s.c.) 1 day before CPP conditioning. In vehicle pretreated rats, administration of gabapentin (50 mg/kg, i.v.) produced significant place preference for the GBP-paired chamber, shown as a positive difference score, suggesting the presence of ongoing pain that is relieved by gabapentin treatment. N = 16, **P = 0.006. By contrast, nor-BNI pretreated animals show no chamber preference, indicating that nor-BNI relieved ongoing pain. N = 13. (C) Representative heat maps demonstrating time spent in different locations in the CPP box on test day. SNL rat pretreated with subcutaneous (s.c.) saline spent more time in the GBP-paired chamber, whereas nor-BNI pretreated rat spent equivalent time in both chambers. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. CPP, conditioned place preference; nor-BNI, nor-binaltorphimine; SNL, spinal nerve ligation.