Figure 3.
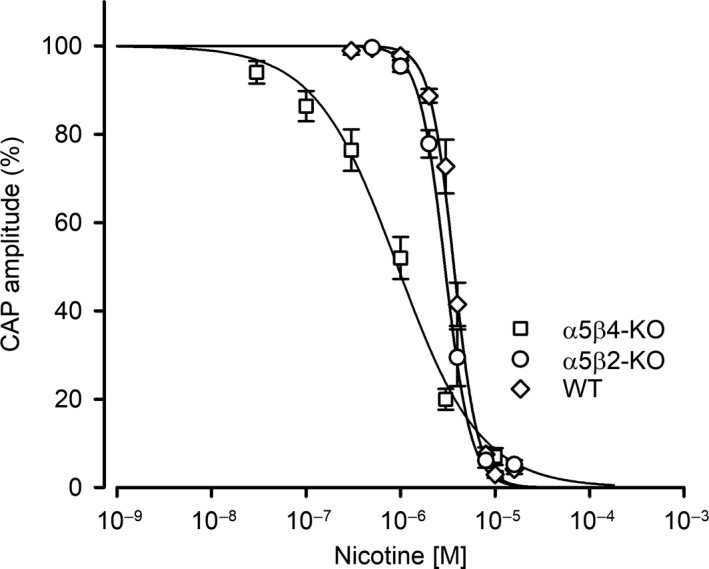
The potency of nicotine at inhibiting CAP amplitude differs between α5β4‐KO, α5β2‐KO, and WT ganglia. Nicotine is more potent at inhibiting CAP amplitude in α5β4‐KO ganglia (squares) compared to both WT (circles) and α5β2‐KO (up‐triangles) ganglia. Nicotine concentration‐response curves show that CAPs following supramaximal stimulation at 0.033 Hz were most potently reduced in α5β4‐KO (IC 50 = 0.93 μmol/L, confidence interval: 0.78–1.11 μmol/L, n = 15), followed by α5β2‐KO (3.01 μmol/L, confidence interval: 2.80–3.23 μmol/L, n = 14) and WT ganglia (3.67 μmol/L, confidence interval: 3.50–3.85 μmol/L, n = 13). The IC 50 values for α5β4‐KO and α5β2‐KO (F 1,145 = 69.1, P < 0.0001, F‐test), and for α5β2‐KO and WT differ significantly (F 1,139 = 21.0, P = <0.0001, F‐test).
