Fig. 1.
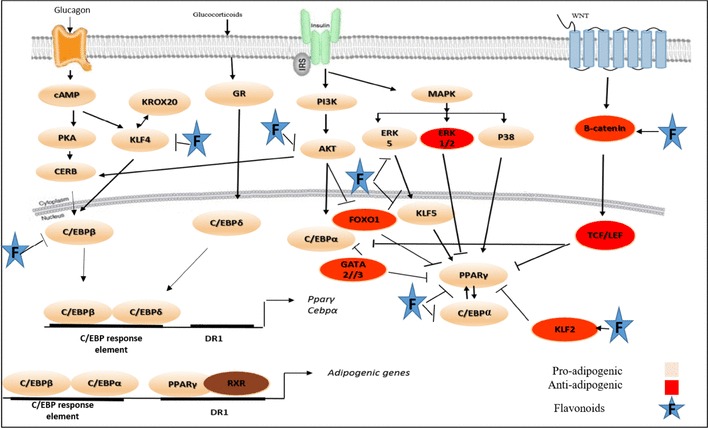
Adipogenesis network. The process of adipogenesis begin with the activation of transcription factors, C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ. These transcription factors function during the early adipogenesis program to regulate the expression of the two master regulators of adipogenesis, PPAR-γ and C/EBPα. The expression of adipogenic genes is regulated by binding of PPARG as a heterodimer with RXRα, where C/EBPα and C/EBPβ occupy the C/EBP response elements. Several other important transcriptional factors play a role in control of adipogenesis. Some transcriptional factors including KLF5 and CREB have a positive role in adipogenesis, whereas other transcriptional factors such as KLF2 and GATA2/3 suppress adipogenesis. C/EBP CCAT/enhancer-binding protein, PPARG peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, KLFs Kruppel-like factors, CREB cyclic AMP response element-binding protein, FOXO1 forkhead box O1, TCF/LEF T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, Wnt wingless-type MMTV integration site family, PKA protein kinase A, GR glucocorticoid receptor, DR1 direct repeat type 1 element
