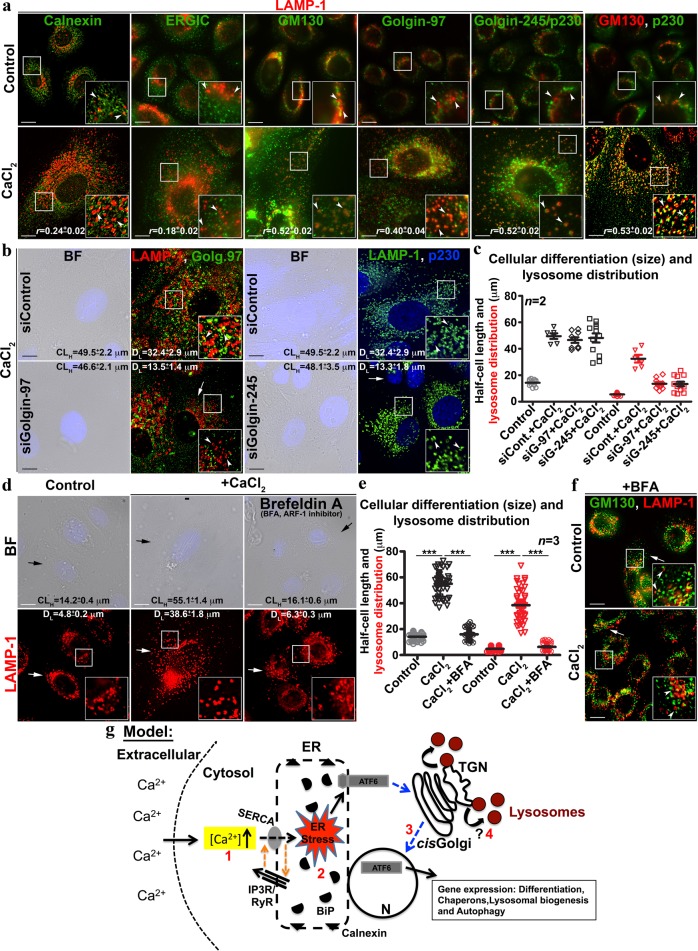
Fig. 5. Keratinocyte differentiation causes fragmentation and dispersal of Golgi and increases colocalization of Golgi tethering proteins with lysosomes. The model illustrating the mechanism of keratinocyte differentiation and lysosome biogenesis.
a IFM analysis of control and differentiated keratinocytes for the localization of ER, transitional ER and Golgi-associated proteins with respect to the lysosomes or the organization of Golgi apparatus (indicated by arrowheads). The degree of colocalization (Pearson’s coefficient, r) between the markers was indicated separately (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3). b BF and IFM images of keratinocytes those were transfected with respective siRNA. White arrows indicate the loss in fluorescence intensity of Golgi-tethering proteins. Arrowheads point to the localization of LAMP-1 with respect to the Golgi-associated proteins. c Quantification of CLH and DL in cells shown in (b). d BF and IFM images of keratinocytes that were treated with brefeldin A (1 μg/ml) alone or with CaCl2 for entire 48 h duration. Black arrows point to the cell limit and white arrows indicate the distribution/morphology of lysosomes. e Quantification of CLH and DL in cells shown in (d). In c and e, both CLH (black symbols) and DL (red symbols) were quantified as μm from the nucleus towards cell surface (~20 cells, n = 2 in c and ~60–80 cells, n = 3 in e) and then plotted. Average CLH and DL (in μm) for each treatment were indicated (mean ± s.e.m.) on IFM images. ***p ≤ 0.001. f IFM analysis of keratinocytes those were described in (d). White arrows indicate the loss in dispersal of Golgi and loss in colocalization between LAMP-1 and GM130. Arrowheads point to the localization of LAMP-1 with respect to GM130. Nuclei are stained with Hoechst 33258 and the insets are magnified view of the white boxed areas. Scale bars, 10 μm. g Model: Prolonged exposure of keratinocytes to CaCl2 increases intracellular calcium [Ca2+] levels (1) within 2 h and possibly elevates ER stress (2) due to altered ER calcium refilling cycle/gradient (orange arrows). Enhanced ER stress promote the Golgi trafficking and processing of ATF6α in to an active UPR TF (3), which possibly initiates the keratinocyte differentiation program. During this process, Golgi compartments merged and generate the enlarged globular lysosomes (4), which probably senses intracellular signaling and balances calcium concentration by acting as reservoir. ? indicates the process requires future investigation