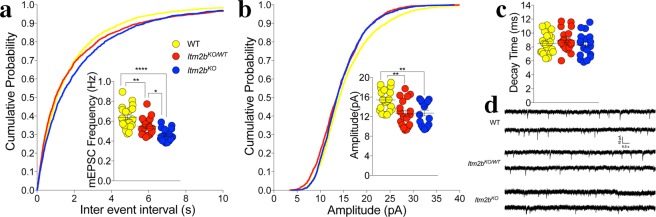
Figure 2.
Loss of Bri2 decreases mEPSC frequency and amplitude at hippocampal SC–CA3 > CA1 synapses. (a) Cumulative probability of a-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4- isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) mediated mEPSC inter-event intervals. Inset in cumulative probability graphs represents average mEPSC frequency. (b) Cumulative probability of AMPAR-mediated mEPSC amplitudes. Inset in cumulative probability graphs represents average amplitudes. (c) Decay time of mEPSC. (d) Representative traces of mEPSCs. Number of mEPSCs recordings were: 21, 18 and 18 for Itm2bWT/WT, Itm2bKO/WT and Itm2bKO mice, respectively All data represent means ± SEM. Data were analyzed by Ordinary one-way ANOVA. ANOVA summary of mEPSC frequency: F = 19.11, adjusted P value < 0.0001 (significant = ****). Post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: WT vs. Itm2bKO/WT adjusted P value = 0.0096 (significant = **); WT vs. Itm2bKO adjusted P value < 0.0001 (significant = ****); Itm2bKO/WT vs. Itm2bKO adjusted P value = 0.9935 (not significant). ANOVA summary of mEPSC amplitude: F = 8.1, adjusted P value = 0.0008 (significant = ***). Post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: WT vs. Itm2bKO/WT adjusted P value = 0.0027 (significant = **); WT vs. Itm2bKO adjusted P value = 0.0038 (significant = **); Itm2bKO/WT vs. Itm2bKO adjusted P value = 0.8245 (not significant). ANOVA summary of mEPSCs decay time: F = 1.011, adjusted P value = 0.3772 (not significant).