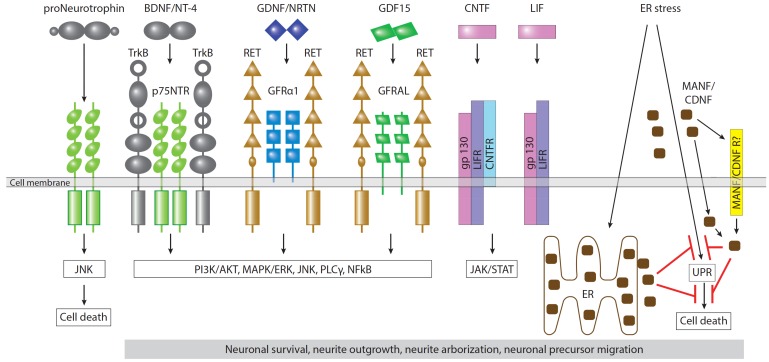
Fig. (2).
Neurotrophic factors and their receptors in dopamine neurons. Dopamine neurons express receptors of neurotrophins (TrkB and p75NTR), GFLs (GFRa and RET), potential distant GFL member GDF15 (GFRAL and RET), neurokines (gp130, LIFR, and CNTFR). Binding of all the afore-mentioned ligands leads to activation of intracellular signaling cascades promoting the survival of neuronal cells, neurite outgrowth and arborization, migration and differentiation of neuronal precursors. MANF and CDNF transmit signals intracellularly via unfolded protein response (UPR) pathways under endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The particular molecular mechanism of action of MANF and CDNF in the cells is poorly understood; however, these proteins can prevent neuronal death induced by ER stress, probably by inhibition of UPR. The ability of MANF and CDNF to protect and restore dopamine neurons when delivered externally implies the existence of a mechanism of their internalization either via yet undiscovered surface receptor (MANF/CDNFR) or via their documented interaction with lipids. Binding of proneurotrophins to p75NTR activates the JNK pathway and leads to cell death. (The color version of the figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).