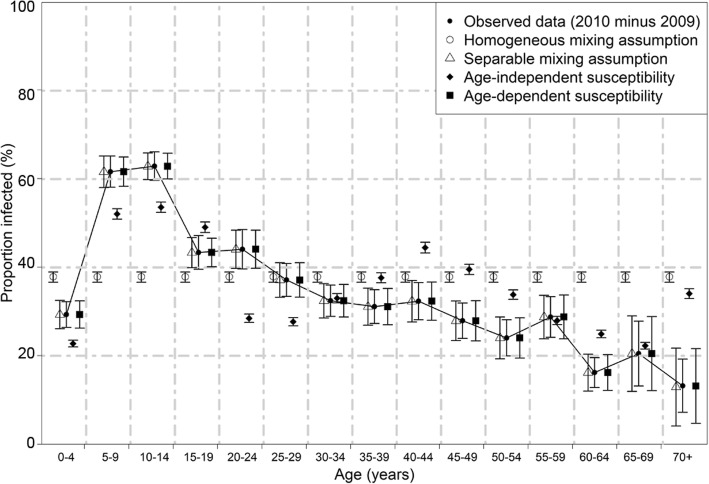
Fig. 4.
Comparison between observed and estimated age-specific proportions of infected individuals during 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic. Age-specific proportions of infection, or the so-called population attack rate or final size, during the 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic, illustrated by age. Estimates were obtained by imposing various assumptions of age-dependent contact patterns, including homogeneous (or random) mixing, separable mixing (i.e., contributions of contactor and contactee are separable), age-independent susceptibility (i.e., the contact matrix was used, but the entire next-generation matrix was assumed proportional to that matrix), and age-dependent susceptibility (i.e., contact matrix plus age-dependent susceptibility per contact were estimated)