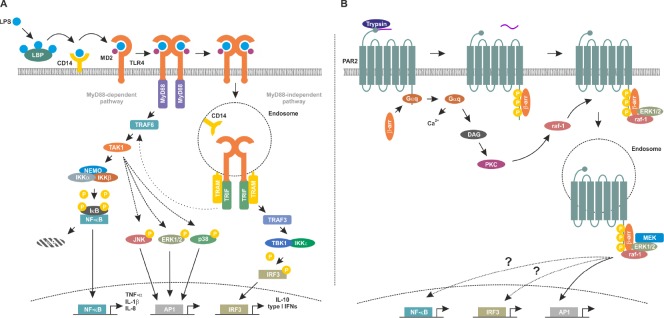
Figure 1.
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) signaling pathways.
(A) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is transferred to TLR4 by CD14 followed by formation of TLR4/myeloid of differentiation protein 2 (MD2) heterotetramers. Membrane-bound TLR4 signaling complex induces the myeloid of differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88)-dependent signaling cascade by recruiting MyD88 and tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor (TRAF)6 which in turn activates transforming growth factor activated kinase-1 (TAK1) and the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase (IKK) complex composed of IKKα, IKKβ and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) essential modulator (NEMO). IKKβ phosphorylates inhibitory inhibitor of κB (IκB) proteins leading to their polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. This frees the DNA binding NF-κB subunits which in turn translocate into the nucleus and modulate expression of the pro-inflammatory target genes including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-8. In contrast, internalised, endosomal TLR4 complex recruits Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR)-domain containing adaptor inducing interferon (TRIF) and TRIF-related adapter molecule (TRAM) activating thereby the MyD88 independent signaling cascade. Subsequently, TRAF3 activates the TRAF family member associated NF-κB activator (TANK)-binding kinase (TBK)1/IKKε which in turn phosphorylates interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 (IRF3) followed by its nuclear translocation and transcription of anti-inflammatory targets including type I interferons and IL-10. Notably, the MyD88 independent signaling cascade also cross-activates NF-κB via interaction between TRIF/TRAM and TRAF6 leading to a weak and late NF- κB activation. (B) Trypsin cleaves PAR2 to expose a new N-terminus which acts as an intramolecular ligand, activating the receptor. Gαq-coupling promotes the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ and production of diacylglycerol (DAG), the latter activating protein kinase C (PKC). Raf-1 is in turn activated by PKC. Activated PAR2 is phosphorylated increasing its affinity for cytosolic β-arrestins (β-arr), which translocate to the cell surface to interact with the receptor. PAR2-boundβ-arrs act as a molecular scaffold recruiting signaling molecules including rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma-1 (raf-1), mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) and extracellular-regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2) at the plasma membrane and in endosomes. Further activation of NF-κB and IRF3 and activating peptide1 (AP1) occurs via as yet undefined mechanisms. Endosomal-activated ERK1/2 promotes AP1 activity. LBP: LPS-binding protein; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase.