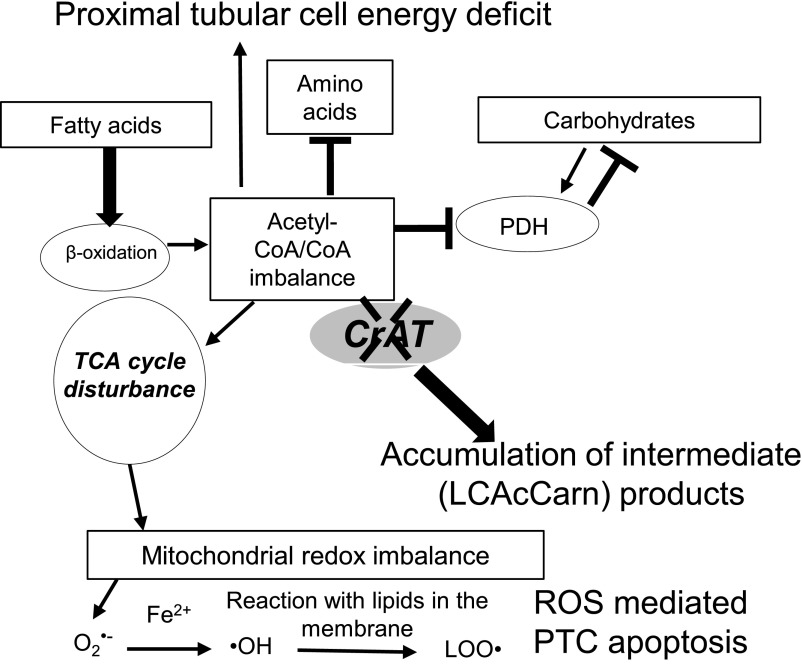
Figure 7.
A proposed scenario of mitochondrial overload in PTCs. Mitochondrial overload modeled by CrAT deletion causes acetyl-CoA/free CoA imbalance and leads to the accumulation of incompletely oxidized products. Such imbalance affects all three major metabolic pathways in PTCs: fatty acid, amino acid, and carbohydrate metabolism. As shown by our mass spectrometry results, overload also affects TCA cycle metabolite levels. Altogether, these metabolic disturbances can contribute to PTC energy deficit. Furthermore, overload can cause mitochondrial redox imbalance through affecting the ETC. Increased ROS and lipid peroxide production then also potentially contributes to PTC apoptosis.