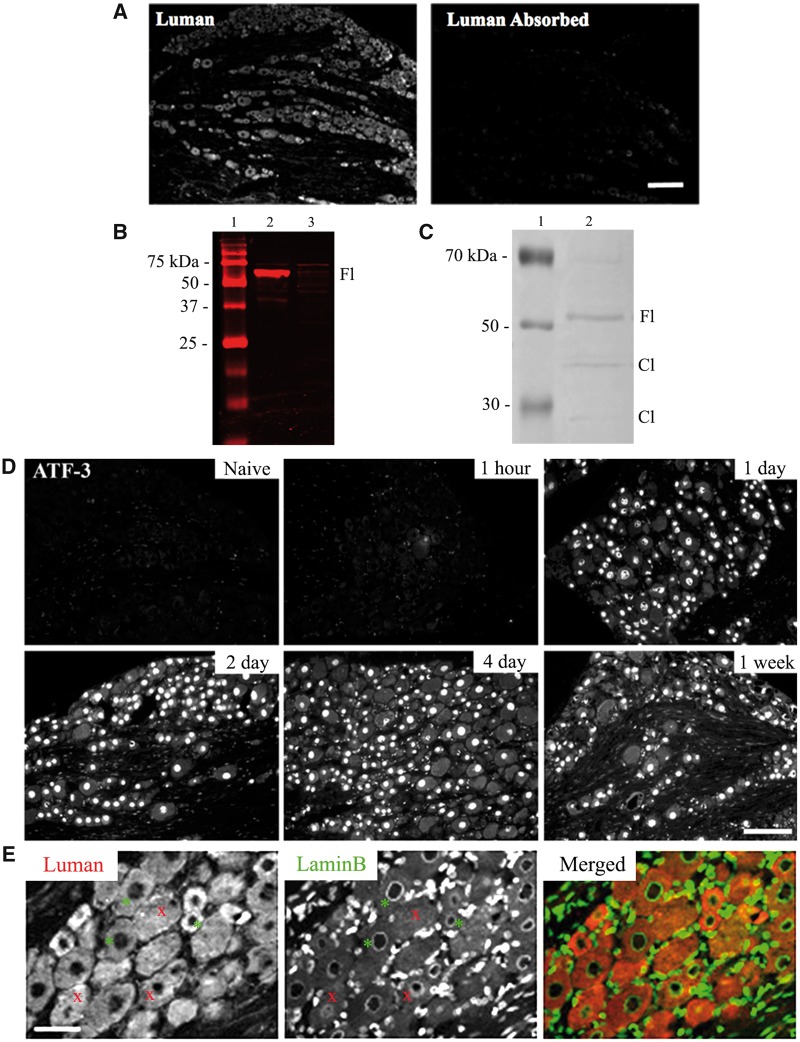
FIGURE 1.
Luman antibody and injury specificity controls. (A) Photomicrographs of L5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) (6-μm sections) processed for immunofluorescence detect Luman protein with anti-Luman rabbit serum (left) and anti-Luman absorbed with cell protein isolates from Luman-transfected Vero cells. Scale bar = 160 μm. Note: Absorption of anti-Luman abolishes immunofluorescence staining. (B) Western blot analysis of anti-Luman rabbit serum-treated membrane of electrophoresed protein extracts from Vero cells transfected with Luman (lane 2) or Zhangfei (lane 3). Molecular weight marker (lane 1). Note: In the Luman-transfected cell extract, anti-Luman recognizes a single band of approximately 60 kDa, the suspected molecular weight of unprocessed Luman, while unable to detect any identifiable antigen in the Zhangfei-transfected cell extract at its expected molecular weight of approximately 30 kDa. (C) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from naïve L4 and L5 DRG (lane 2). Molecular weight marker (lane 1) Note: Anti-Luman recognizes unprocessed full-length Luman (Fl) at approximately 60 kDa and 2 additional faint bands of approximately 40 and 15 kDa, the predicted molecular weights of Luman protein cleavage products (Cl). (D) L5 DRG sections (6 μm) processed to detect injury-associated ATF-3 protein in DRG sections ipsilateral to 1-hour, 1-day, 2-day, 4-day, and 1-week L4–L6 spinal nerve transection or naïve controls. Scale bar = 150 μm. Injury state is confirmed by presence of nuclear ATF-3 immunofluorescence, detectable by 1-day post-injury. (E) To accurately delineate cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments, all tissue was dually processed for Luman (red) and LaminB (green) immunofluorescence, the latter recognizing the nuclear envelope. Only neurons with a clearly defined LaminB ring were analyzed (examples-*), as they identify cells sectioned through their center with clear cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments; those without defined rings were not (examples-x). Scale bar = 75 μm.