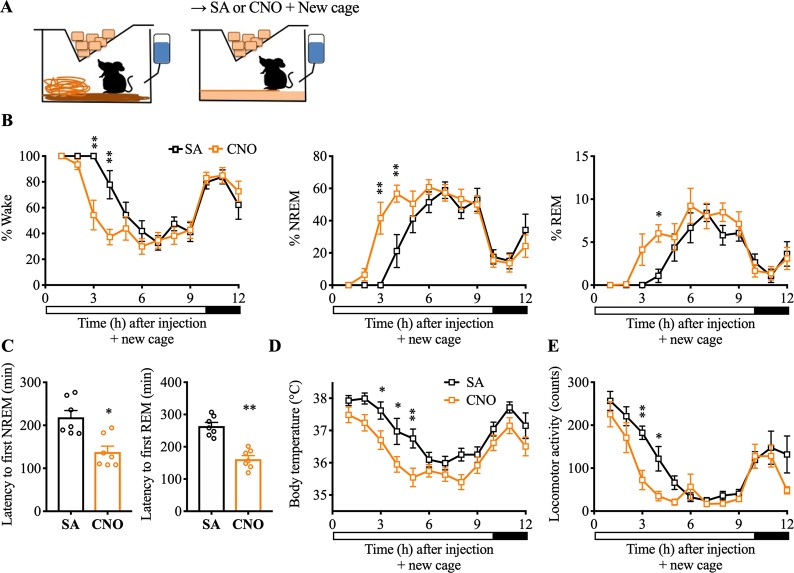
Fig 7. Chemoinhibition of NtsLH neurons attenuates stress-induced arousal and hyperthermia.
(A) Schematic of novel environment experimental setup. Mice were introduced to a new cage with fresh nesting material immediately after i.p. injections of saline or CNO at 9:50 AM. Hourly percentages of sleep-wake stages (B), mean Tb (D), and total LMA counts (E) for 12 h after saline or CNO (1.5 mg/kg) administration and cage change. Two-way RM ANOVA for the first 12 h after treatment for “time” and “compound injected,” followed by Sidak post hoc test (n = 7 mice; for wake: interaction F(11, 72) = 3.20, P = 0.0014, compound injected F(11, 72) = 24.15, P < 0.0001, time F(1, 72) = 9.97, P = 0.0023; for NREM: interaction F(11, 72) = 3.20, P = 0.0014, compound injected F(11, 72) = 23.37, P < 0.0001, time F(1, 72) = 9.39, P = 0.0031; for Tb: time F(1, 72) = 55.44, P < 0.0001, compound injected F(11, 72) = 12.13, P < 0.0001; for REM: interaction F(11, 72) = 1.43, P = 0.18, compound injected F(11, 72) = 12.82, P < 0.0001, time F(1, 72) = 7.45, P = 0.0080; for Tb: interaction F(11, 72) = 0.93, P = 0.51, compound injected F(11, 72) = 12.13, P < 0.0001, time F(1, 72) = 55.44, P < 0.0001; for LMA: interaction F(11, 72) = 1.92, P = 0.051, compound injected F(11, 72) = 18.43, P < 0.0001, time F(1, 72) = 18.12, P < 0.0001). (C) NREM and REM sleep latencies after saline or CNO injections and cage change: Mann–Whitney test (n = 7 mice; for NREM: P = 0.011; for REM: P = 0.0006). Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. When placed into the new cage during their rest period, mice display increased wake, hyperactivity, and hyperthermia for 3–4 h before they go to sleep. Chemoinhibition of NtsLH neurons attenuates these responses to the novel environment stress. The underlying data for this figure are available from the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/nmrpq/). CNO, clozapine-n-oxide; i.p., intraperitoneal; LH, lateral hypothalamic area; LMA, locomotor activity; NREM, non-rapid eye movement; Nts, neurotensin; REM, rapid eye movement; RM, repeated measures; SA, saline; Tb, body temperature.