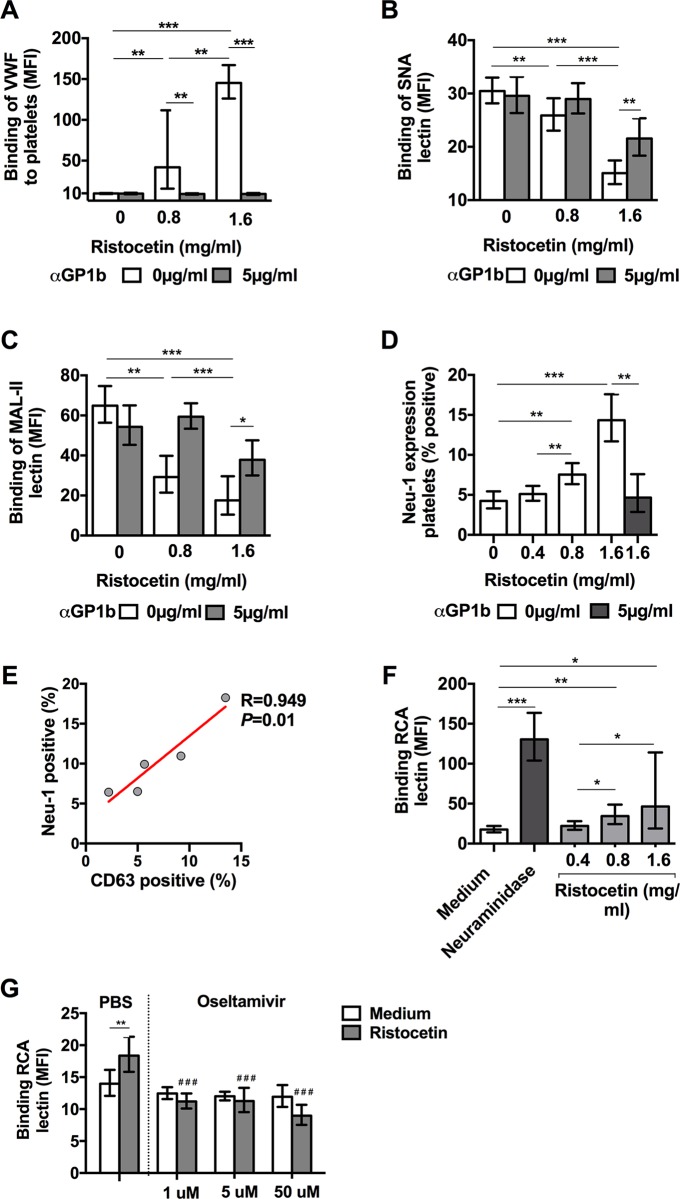
Fig 5. Binding of VWF to platelets induces platelet desialylation which can be inhibited by oseltamivir.
Binding of (A) von Willebrand factor (VWF), (B) SNA and (C) MAL-II lectins to platelets and (D) platelet membrane expression of Neuraminidase-1 (Neu-1) after exposing platelet rich plasma (PRP) of healthy volunteers to ristocetin for 1 hr at 37°C in presence and absence of GPIb receptor blocking antibodies. (E) Pearson correlation between the expression of Neu-1 and the lysosomal marker CD63 on the platelet membrane after incubation PRP with ristocetin (1.6mg/ml for 1 hour). (F) Binding of RCA lectin to galactose or N-acetylgalactosamine residues on platelets after exposing PRP to ristocetin (G) with and without the addition of increasing concentration of oseltamivir. Purified neuraminidase from C. perfringens (100mU) was used as a positive control. Data were analyzed using Student’s T-tests and presented as geometric mean with 95% confidence interval. *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.005, * P < 0.05; ### P < 0.001 when samples were compared with ristocetin-treated samples that were unexposed to oseltamivir. Data were from on 5–7 platelet donors in ≥ 2 independent experiments.