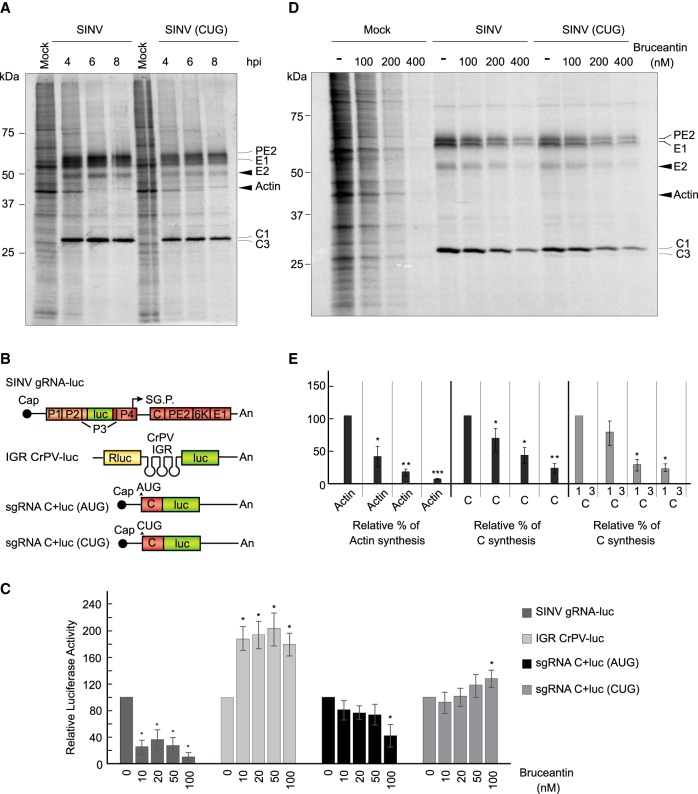
FIGURE 8.
Bruceantin differentially affects cellular and viral protein synthesis. (A) BHK cells were mock infected or infected with 10 plaque-forming units/cell wt SINV or SINV (CUG). Then, the medium was changed to a labeling medium with [35S] Met/Cys to detect the proteins synthesized during the next hour at the indicated times post-infection. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and fixed and labeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. Synthesized viral proteins C, PE2, E1 and E2 are indicated in the gel as well as cellular actin. (B) Schematic representation of the in vitro transcribed mRNAs: SINV gRNA-luc, IGR CrPV-luc, sgRNA C + luc (AUG), and sgRNA C + luc (CUG). (C) RRL were pretreated or not with the indicated concentrations of bruceantin for 20 min. Subsequently, 100 ng SINV gRNA-luc, IGR CrPV-luc, as controls, and sgRNA C + luc (AUG) and sgRNA C + luc (CUG) mRNAs were added and incubated for 90 min at 30°C. Luciferase synthesis was estimated by measuring luciferase activity. The values shown are percentages of the value of their respective nontreated counterparts and are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated compared to each respective control using Student's t-test, and is shown as (*) P < 0.05. (D) BHK cells mock infected or infected with 10 plaque-forming units/cell wt SINV or SINV (CUG) were maintained in growth medium for 7 h. The medium was then changed to a labeling medium and cells were nontreated or treated with different amounts of bruceantin for 15 min before addition of [35S] Met/Cys to detect the proteins synthesized during the next hour. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and fixed and labeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. The viral proteins C, PE2, E1, and E2 are indicated in the gel and also the cellular actin. (E) Densitometric analysis of protein synthesis. In mock-infected cells, the level of actin was used to determine the effect of bruceantin in treated versus untreated cells. In cells infected with wt SINV or SINV (CUG), protein C was used to determine the inhibitory effect of the compound by comparing the amounts present in treated cells versus their nontreated counterparts. The results are displayed as mean ± SD of three representative experiments.