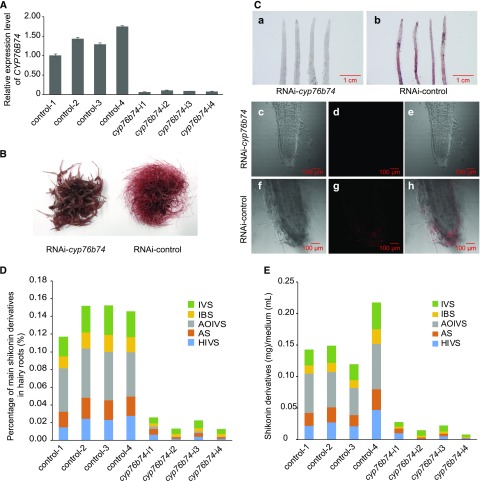
Figure 5.
Physiological function of CYP76B74 in vivo. A, Expression levels of CYP76B74 in hairy roots of the four independent RNAi-cyp76b74 lines and the control. B, Phenotypes of RNAi-cyp76b74 lines and the control cultured for 10 d in liquid medium. C, Phenotypes of RNAi-cyp76b74 lines and the control cultured on a plate using a stereoscopic microscope (a and b) and the root tips by two-photon confocal microscopy (c–h). c and f, Bright-field microscopy of root tips; d and g, shikonin autofluorescence field microscopy of root tips; e and h, merged fields of bright-field and shikonin autofluorescence. D, Percentage of main shikonin derivatives in the dry weight of the four independent RNAi-cyp76b74 hairy root lines and the control. E, Contents of main shikonin derivatives in culture medium of the four independent RNAi-cyp76b74 hairy root lines and the control. IVS, Isovalerylshikonin; IBS, isobutyrylshikonin; AOIVS, acetoxylisovalerylshikonin; AS, acetylshikonin; HIVS, β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin.