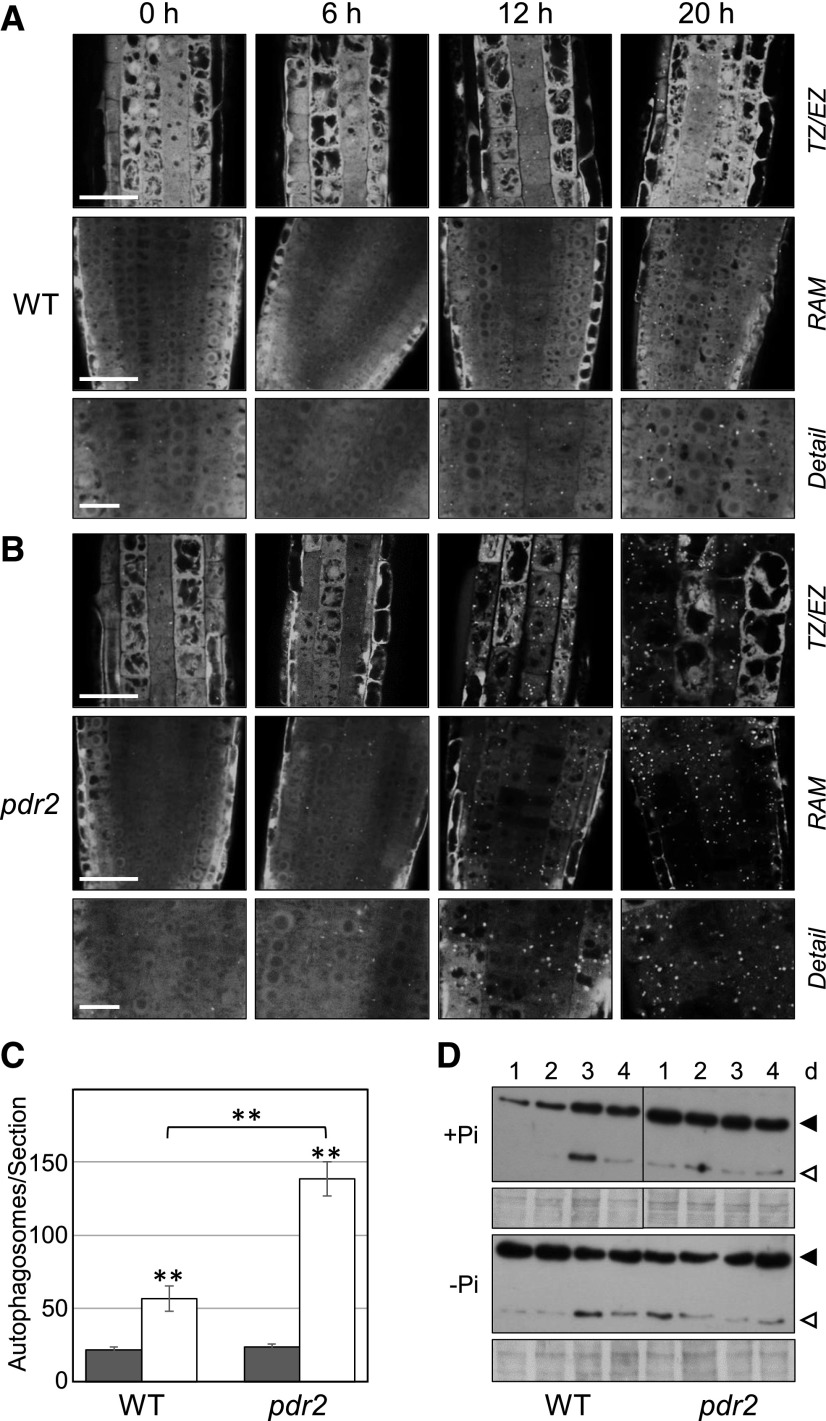
Figure 1.
Phosphate (Pi) limitation activates autophagy in the root apex. A and B, Detection of GFP-ATG8–labeled autophagosomes in Pi-deprived root tips. GFP-ATG8a-derived fluorescence in primary root meristems of the transgenic (p35S::GFP-ATG8a) Col-0 wild-type (WT) (A) and pdr2 (B) seedlings after germination on +Pi agar (4 d) and subsequent transfer to –Pi medium for 0 to 20 h. Right labels show that in (A) and again in (B) are representative images of the transition zone (TZ) and early elongation zone (EZ) (upper row), the RAM (middle row), and detail of the RAM (lower row). Scale bars = 50 µm (TZ/EZ, RAM) and 20 µm (detail). C, Quantification of GFP-labeled puncta (number of autophagosomes per section) 20 h after transfer from +Pi to +Pi (black bars) and from +Pi to –Pi (white bars) media (±se; n ≥ 15; **, P ≤ 0.01). D, Detection by immunoblot analysis (anti-GFP antibodies) of free GFP (open triangle) derived from GFP-ATG8a (solid triangle) expressed in the primary roots of the transgenic wild-type and pdr2 seedlings upon their transfer (germinated for 4 d on a +Pi medium) to either +Pi or –Pi medium for up to 4 d. Coomassie blue-stained total proteins are shown below the blots to indicate the amount of protein loaded per lane. Images of the +Pi transfer experiment were derived from the same gel/probed membrane but cropped to remove the central marker lane.