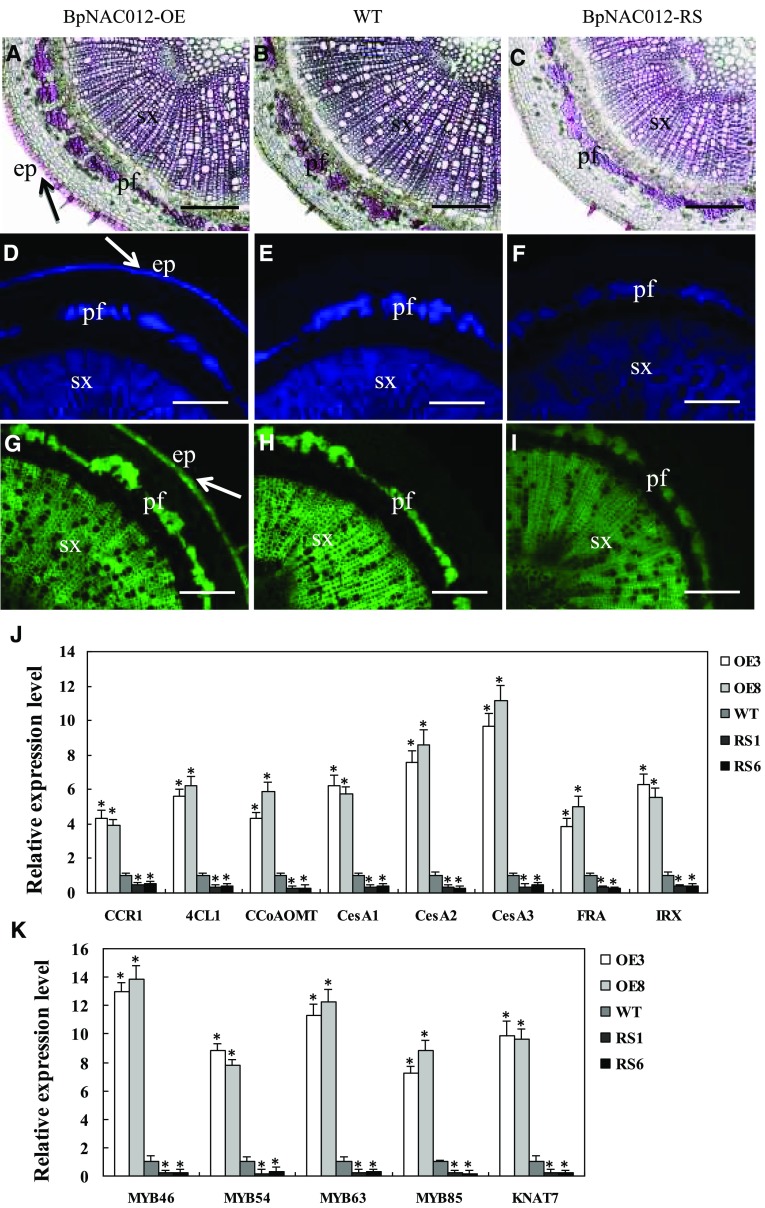
Figure 7.
Detection of lignin, cellulose, and xylan in stem sections of BpNAC012 transgenic birch. A to C, Phloroglucinol-HCl staining of lignin in stem sections of the BpNAC012-OE (A), wild-type (WT; B), and BpNAC012-RS (C) plants. The arrow shows intensive lignin staining in the walls of the epidermis. D to F, Calcofluor White staining of cellulose in stem sections of the BpNAC012-OE (D), wild-type (E), and BpNAC012-RS (F) plants. The arrow shows intensive cellulose staining in the walls of the epidermis. G to I, Detection of xylan in stem sections of the BpNAC012-OE (G), wild-type (H), and BpNAC012-RS (I) plants probed with the LM10 xylan monoclonal antibody. The arrow shows intensive xylan staining in the walls of the epidermis. ep, Epidermis; pf, phloem fiber; sx, secondary xylem. Bars = 100 μm. J, Expression analysis of secondary wall biosynthetic genes, including lignin biosynthetic genes (CCR1, 4CL1, and CCoAOMT), cellulose synthases (CesA1, CesA2, and CesA3), and xylan biosynthetic genes (FRA and IRX), in the stems of BpNAC012-OE and BpNAC012-RS plants compared with the wild type. K, Expression analysis of secondary wall transcription factor genes (MYB46, MYB54, MYB63, MYB85, and KNAT7) in the stems of BpNAC012-OE and BpNAC012-RS plants compared with the wild type. The expression level of each gene in the wild type was set to 1. Error bars represent the sd of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the wild type and the transgenic lines at the 0.05 level by one-way ANOVA.