Fig. 5. HTS strategy of GSK compound library.
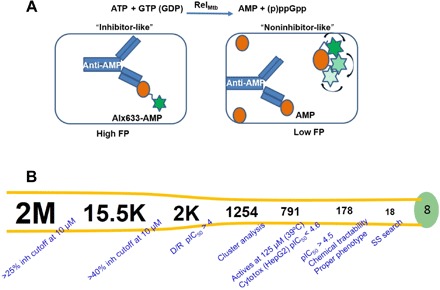
(A) Target inhibition assay using truncated RelMtb. (B) Flowchart of RelMtb inhibitor screen, yielding 178 hits and representing eight distinct families. Over 2 million compounds were tested at 10 μM. The 15,463 primary hits were retested for confirmation at 10 μM. The 2084 active and chemically attractive compounds were generated for progression into dose-response studies. Eighty-three percent of the selected compounds showed activity. These compounds were clustered to evaluate the chemical diversity of the set. Approximately 750 hits with appropriate physicochemical properties, belonging to different chemical classes, were identified showing inhibitory concentration (pIC50) values of >4.5 and no artifactual effect. About 50 additional compounds were rescued with an MW of >600 and a clogP of >6.5 by manual inspection. A total of 791 compounds were profiled in whole-cell assays to identify hits yielding the Δrel phenotype during heat stress. One hundred seventy-eight compounds showed inhibition at 125 μM against Mtb during exposure to elevated temperature with no or moderate toxicity against HepG2 cells (pIC50 < 4.6). Compounds with minimum inhibitory concentration ratios greater than twofold against WT Mtb versus Δrel were grouped into 18 structurally diverse classes. These hits were expanded through a series of analogs, which were tested in the biochemical RelMtb and HepG2 assays. Further phenotypic characterization was performed with a selection of the most promising compounds from each family. The remaining eight families (GSK-A, GSK-B, GSK-C, GSK-D, GSK-H, GSK-I, GSK-K, and GSK-M) were selected for further studies. Inh, inhibition; D/R, dose-response; SS, substructure.
