Fig. 3. Prelamin A preferentially down-regulates CK2 activity over lamin A.
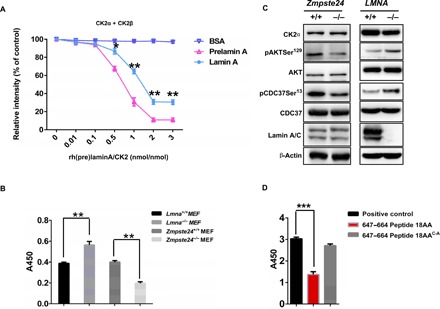
(A) CycLex CK2 assay to detect CK2 enzyme activity. rh(pre)laminA protein was incubated with CK2 in vitro. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as a control. Statistical analysis showing lamin A inhibits CK2α/β activity in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of prelamin A on inhibiting CK2α/β activity is stronger than that of lamin A. The data (means ± SEM) represent three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t test. (B) CK2 enzyme activity in Zmpste24−/− MEFs and Lmna A−/− MEFs. CK2 enzyme activity was decreased in Zmpste24−/− MEFs and increased in Lmna−/− MEFs compared to WT littermate controls. The data (means ± SEM) represent three independently derived lines of MEFs in separate experiments. **P < 0.01. (C) Representative Western blots showing protein levels of CK2α and its downstream target proteins, pAKTSer129 and pCDC37Ser13, which reflect CK2 activity in vivo, in Zmpste24−/− MEFs and WT littermate controls. (D) CycLex CK2 assay to detect CK2 enzyme activity by incubation with synthesized WT prelamin A (amino acids 647 to 664) peptide and C661A mutant peptide. All MEFs were used at passage 4. Data represent three independently derived lines of MEFs in separate experiments. ***P < 0.001.
