Fig. 2. KDS2010 is a potent, selective, and reversible MAO-B inhibitor.
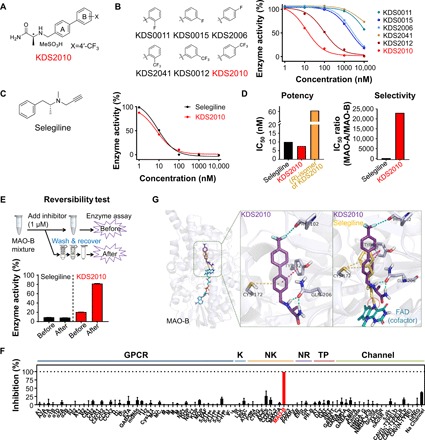
(A) Chemical structure of KDS2010. (B) Chemical structures and concentration-enzyme activity curves of the selected KDS derivatives in the MAO-B enzyme assay (n = 4 assays). (C) Comparison to the well-known irreversible MAO-B inhibitor. Left: Chemical structure of selegiline. Right: Concentration-enzyme activity curves for selegiline and KDS2010 in the MAO-B enzyme assay (n = 4 assays). (D) Potency and selectivity of selegiline and KDS2010 based on IC50 (in nM) levels of MAO-B and the isoform MAO-A. (E) Top: Diagram of the reversibility assay protocol. Bottom: Enzyme activity normalized to the dimethyl sulfoxide–treated group at each “before” and “after” step. (F) The off-target selectivity for 87 primary molecular targets at 1 μM KDS2010. A significant response (≥50% inhibition for biochemical assays) was only observed for MAO-B (>99% inhibition; n = 2 assays; red bar). GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; K, kinase; NK, non-kinase; NR, nuclear receptor; TP, transporter; Channel, ion channel. See table S4 for the detailed results. (G) Left: Binding position of selegiline (yellow), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) (cyan), and KDS2010 (purple) inside the MAO-B binding pocket. Middle: Molecular interactions of KDS2010 are indicated by the dashed line [halogen bond (cyan), π-sulfur interaction (yellow), π-π T-shaped (magenta), and hydrogen bond (green)]. Right: Selegiline was covalently bound to FAD, an MAO-B cofactor (red dotted circle).
