FIG 1.
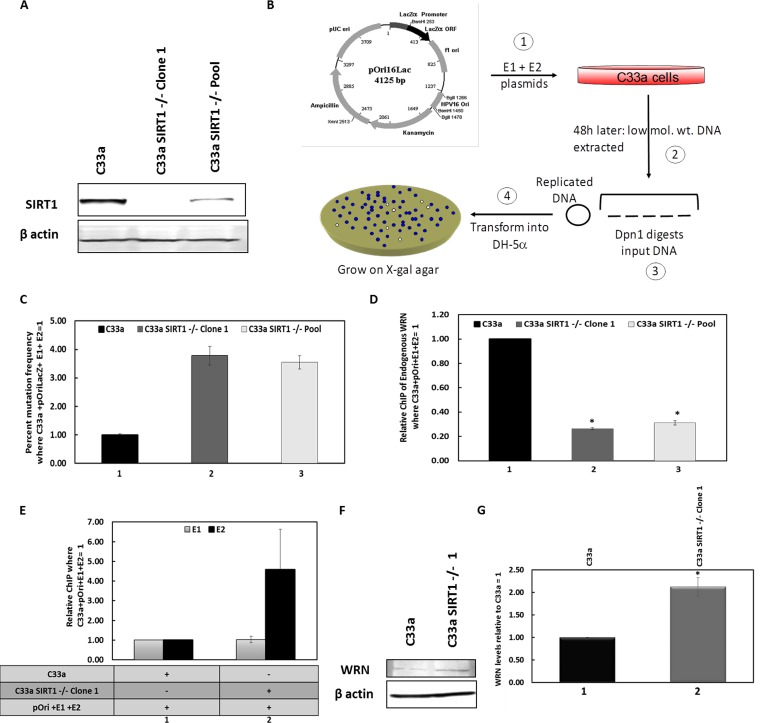
Absence of SIRT1 results in mutagenic E1-E2 DNA replication and a reduction in recruitment of WRN to the replicating DNA. (A) C33a cells with CRISPR/CAS9 editing of SIRT1 expression demonstrate a reduction in SIRT1 expression in a clonal line (Clone 1) and in pooled cells (Pool). (B) Graphic description of our E1-E2 mutagenesis assay, a key component of this report. ORF, open reading frame; ori, origin of replication. In step 1, E1 and E2 expression plasmids are cotransfected with pOri16Lac, which contains the HPV16 origin of replication and the lacZ gene. In step 2, 48 h later, low-molecular-weight (low mol. wt.) DNA is harvested from the cells and digested with DpnI (3), which digests the transfected DNA but not the replicated DNA. The replicated DNA is then transfected into DH10B or DH5α cells (4) and plated on agar with X-gal and kanamycin. White colonies indicate replicated molecules that have picked up mutations in the lacZ gene (66). (C) E1-E2 DNA replication in the absence of SIRT has a significantly enhanced mutagenic phenotype. In both C33a SIRT1–/– clone 1 and pool cells, there is an enhanced mutagenesis compared with that of wild-type cells (compare lanes 2 and 3 with lane 1). This increase is statistically significant (P value is less than 0.05), and standard error bars are shown. In the absence of E1 or E2, there are no bacterial colonies detected, as there is no replication. The histogram depicts the results of three independent experiments. (D) In the absence of SIRT1, there is a reduction in recruitment of WRN to the E1-E2-replicating DNA. Chromatin was prepared from the cells, and ChIP assays were carried out with a WRN antibody; the results are expressed relative to the levels in wild-type C33a cells, which equal 1. The results presented are a summary of results from three independent experiments. Figure S1B and C describe the controls for these experiments. The reduction in WRN recruitment is statistically significant, as indicated with an asterisk (the P value was less than 0.05), and standard error bars are shown. (E) There is no significant difference in E1 and E2 recruitment to the replicating DNA in the absence of SIRT1, although E2 levels do trend higher, presumably due to the elevated levels of E2 in the absence of SIRT1 (41). Shown is a summary of the results from at least 3 independent experiments, and standard error bars are presented. (F) In the absence of SIRT1, there is an increased level of endogenous WRN. (G) This experiment was repeated, and the results were quantitated; there is a significant increase (*) of WRN in the absence of SIRT1 (P value was less than 0.05; standard error bars are shown).