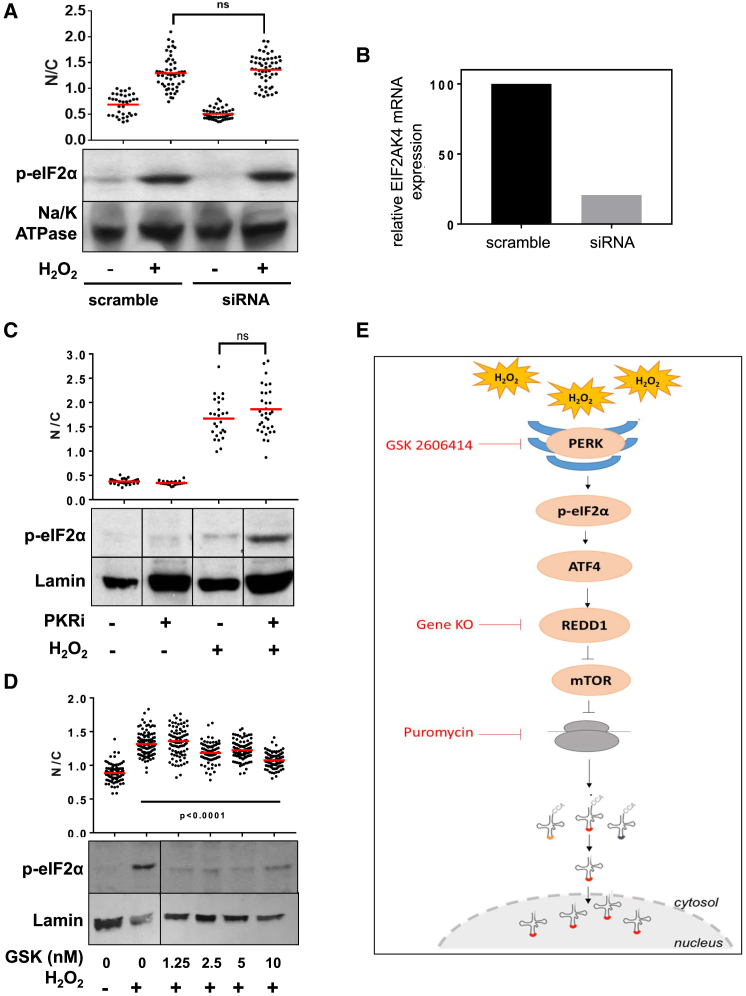
Figure 7.
PERK Regulates tRNA Retrograde Transport
(A) Top: cells treated with siRNA targeting GNC2 (EIF2AK4) or with scrambled siRNA were incubated with 5 mM H2O2 for 2 h, and tRNA nuclear accumulation was detected by tFISH and quantified by ImageJ. Bottom: western blot showing S51 phosphorylation of eIF2α in the presence or absence of H2O2 in mock and GCN2/EIF2AK4-depleted cells.
(B) qRT-PCR to detect EIF2AK4 mRNA in cells transfected with the targeting or scrambled siRNAs.
(C) Top: cells were treated with 5 mM H2O2 for 2 h in the presence or absence of the imidazole-oxindole PKR inhibitor C16 (PKRi, 300 nM), and tRNA nuclear accumulation was detected by tFISH and quantified by ImageJ. Bottom: S51phosphorylation of eIF2α was detected by western blot, and lamin was used as a loading control.
(D) Top: cells were incubated with 5 mM H2O2 for 2 h in the presence of different concentration of the PERK inhibitor GSK 2606414 (GSK), and tRNA nuclear accumulation was detected by tFISH and quantified by ImageJ. Bottom: S51 phosphorylation of eIF2α was detected by western blot, and lamin was used as a loading control.
(E) Schematic summary of the pathways regulating tRNA retrograde transport.
Statistical significance was calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (A and C) or by one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test) (D).