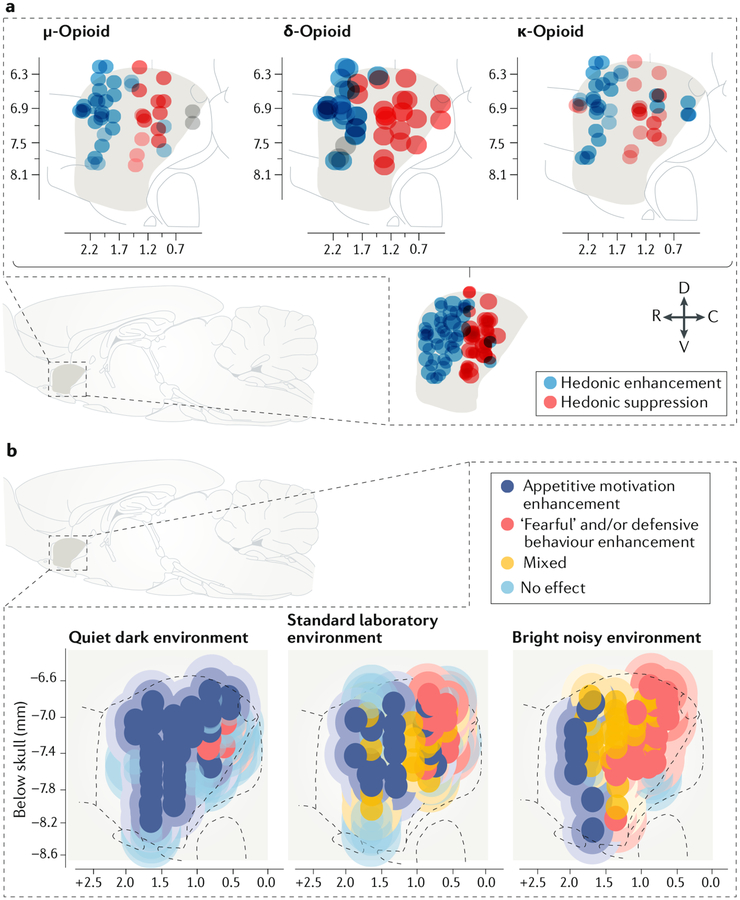
Fig. 2 |. Evidence for affective modules and affective modes in the nucleus accumbens.
a | A sagittal view of the medial shell of the rat nucleus accumbens shows the rostrodorsal ‘hedonic hot spot’, here revealed as the sites at which microinjections of μ, δ or κ-opioid receptor agonists all enhanced the hedonic impact of sucrose (blue circles; enhancement defined as 200–300% increases in taste-elicited orofacial ‘liking’ reactions)2,62. The axis numerals mark stereotaxic coordinates relative to Bregma. Conversely, in a caudal ‘hedonic cold spot’, the same opioid microinjections suppressed ‘liking’ reactions by ~50% (red circles). The bottom section shows the location of a shared opioid hot spot for hedonic enhancement and shared cold spot for hedonic suppression. b | A sagittal view of the rat nucleus accumbens shows a bivalent rostrocaudal gradient pattern of affective modules in the medial shell, revealed by microinjections of a glutamate AMPA receptor antagonist. Dark blue circles indicate microinjection sites that produced selective increases in appetitive motivation to eat food41 (similar results were shown in REF.23). Yellow circles show microinjection sites that enhanced both mixed appetitive and defensive behaviours, with these behaviours typically alternating in the same rat in the hour after microinjection. Red circles show microinjection sites that enhanced only actively defensive or ‘fearful’ behaviours. This study revealed shifts of the valence function of many microinjection sites driven by changes in environmental ambience. When rats were tested in a quiet, dark home environment, microinjection at most sites enhanced only appetitive behaviour. In a standard laboratory environment with moderate illumination and background sound levels, the nucleus shell was evenly divided between rostral appetitive, central mixed and caudal defensive zones. In a stressful highly illuminated and noisy laboratory environment, defensive and mixed zones expanded whereas the appetitive zone shrank to only the far-anterior edge. C, caudal; D, dorsal; R, rostral; V, ventral. Part a republished with permission of the Society for Neuroscience, from Opioid hedonic hotspot in nucleus accumbens shell: Mu, delta, and kappa maps for enhancement of sweetness “liking” and “wanting”. Castro, D. C. & Berridge, K. C. 34(12), 2014; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. (REF.62). Part b is adapted from REF.41, Springer Nature Limited.