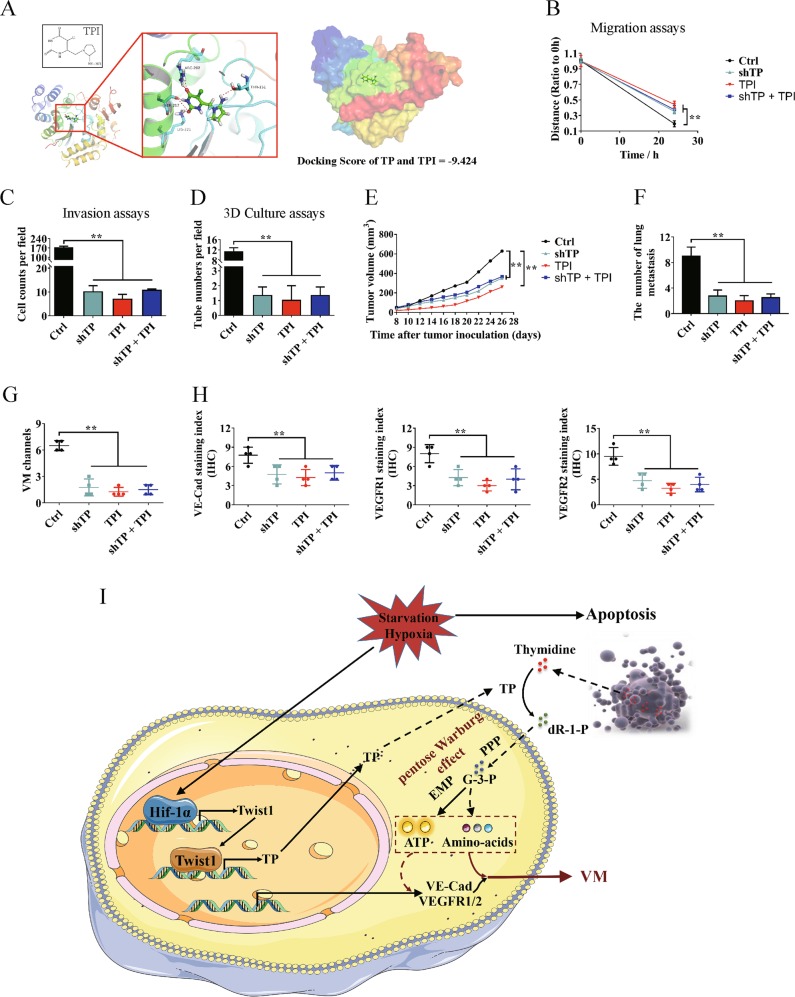
Fig. 7. Effects of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) enzyme inhibitor on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and metastasis.
Hep3B cells were treated by knocking down TP and/or adding TP enzyme inhibitor tipiracil (TPI). a TPI exhibited good binding activity to TP determined by molecular docking. b Wound healing assay was performed. Quantitative analysis showed a significant difference in the speed of migration among different treated Hep3B cells. c Invasion assay showed a significant difference in the speed of invasion among different treated Hep3B cells. d Knocking down TP and/or adding TPI inhibited tube formation as detected by three-dimensional culture assay. e Effects of knocking down TP and/or adding TPI on Hep3B xenograft tumor growth. f Number of tumor formations and lung metastasis in different groups. Images were taken at ×100 magnification. g Statistical analysis of VM formation in different treated Hep3B xenograft tumors. h Statistical analysis of VE–Cad, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), and VEGFR2 expression levels in different treated Hep3B xenograft tumors. i Proposed regulatory mechanism between Twist1–TP and VM in HCC. (mean ± SD; **P < 0.01)