Fig. 2.
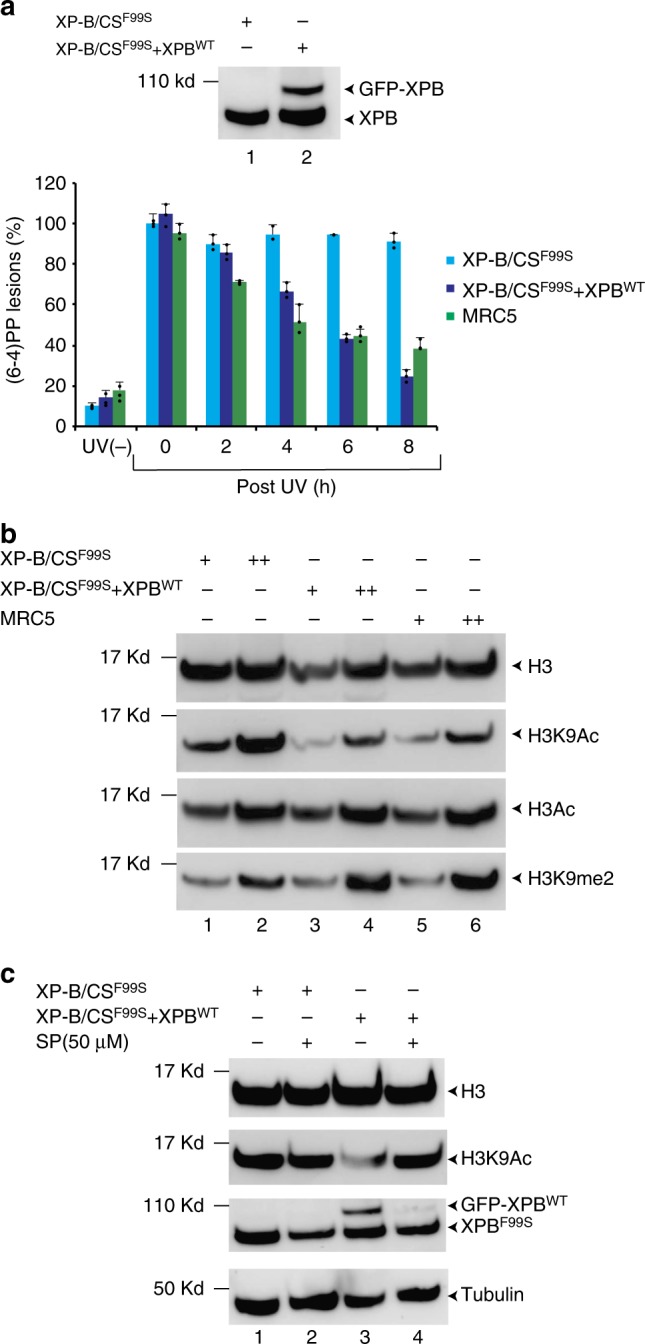
XP-B/CSF99S patient-derived cells have a global increase in the H3K9ac histone mark. a Extracts from either XP-B/CSF99S or XP-B/CSF99S + XPBWT cells were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with a monoclonal mouse anti-XPB antibody. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. (6-4)PP removal measurements were carried out in XP-B/CSF99S, stably transfected XP-B/CSF99S + XPBWT and wild-type MRC5 cells harvested at different time points after UV irradiation at 30 J/m2 as indicated. Cells were labeled with a monoclonal mouse anti-(6-4)PP antibody and signals were measured using a INCell 1000 analyzer (GE Healthcare). The graph represents the percentage of lesions remaining in the genome at a given time (error bars represent SD from three independent experiments). For each time point, about 20000–40000 cells were analyzed. b Histones were extracted from either XP-B/CSF99S, XP-B/CSF99S + XPBWT or wild-type MRC5 fibroblasts, resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with either polyclonal rabbit anti-histone H3, polyclonal rabbit anti-histone H3ac, monoclonal mouse anti-histone H3K9ac or polyclonal rabbit anti-histone H3K9me2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c XP-B/CSF99S or XP-B/CSF99S + XPBWT cells were treated 3 h with DMSO or SP (50 μM) and histones were extracted, resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted either with a polyclonal rabbit anti-histone H3 or with monoclonal mouse anti-histone H3K9ac antibodies. In parallel, cell extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and western blotted with either a monoclonal mouse anti-XPB or polyclonal rabbit anti-tubulin antibodies. Source data are provided as a Source Data file
