Figure 2.
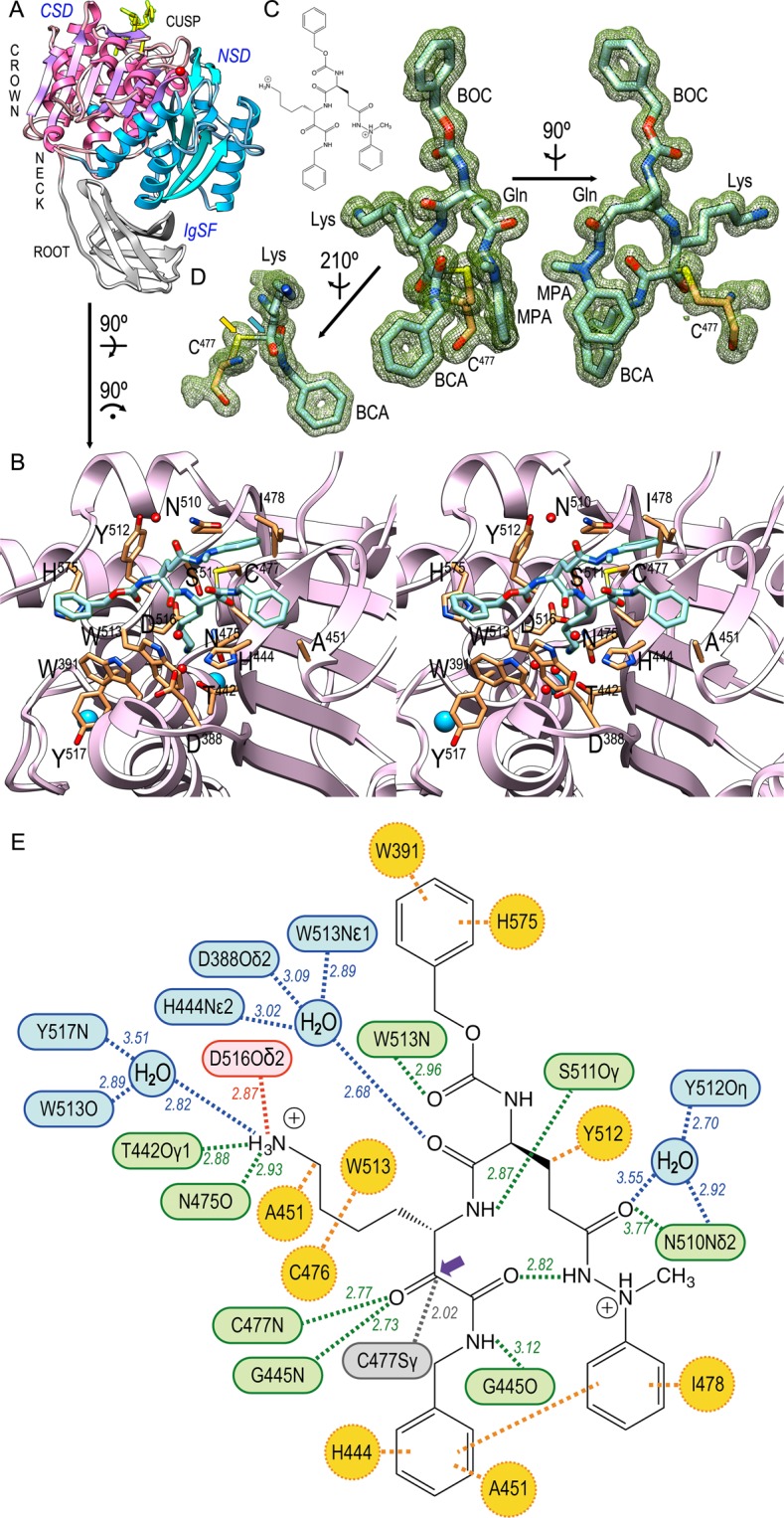
Interactions of the Kgp·KYT-36 complex. (A) Ribbon plot of Kgp, which mimics a tooth, whose crown encompasses the cusp in the top and consists of the NSD (blue ribbon) and CSD domains (magenta ribbon). Domain IgSF (grey ribbon) features the tooth root. KYT-36 is displayed as yellow sticks for reference. (B) Close-up of the tooth cusp encompassing the active site. The cleft runs from left (non-primed sub-sites) to right (primed sub-sites). Only the CSD is displayed as a plum ribbon for clarity. Kgp residues relevant for the complex are shown for their side chains (carbons in sandy brown) and labeled. The proposed catalytic triad is C477, H444 and D388 30. Solvent molecules and structural sodium cations are depicted as red and blue spheres, respectively. KYT-36 is shown as a stick model with carbons in light blue. (C) Structure of KYT-36 and Kgp catalytic residue C477 superposed with a (2mFobs-DFcalc)-type Fourier map contoured at 0.8σ (left) and after a 90°-rotation (right). The five moieties of the inhibitor (see Fig. 1) are labeled. The inset in the top left depicts the chemical structure of the inhibitor for reference. (D) Detail of (C, left) after reorientation depicting the pseudo-covalent bond (2.02 Å) between C477Sγ (yellow arrow) and the carbonyl carbon of LYS (blue arrow), which mimics the scissile carbonyl carbon of a substrate and is pyramidalized. (E) Scheme with the average distance values of direct (green) and solvent-mediated (blue) hydrogen bonds, salt bridges (red), hydrophobic interactions (orange), and the pseudo-covalent bond between the LYS carbonyl carbon (purple arrow) and catalytic C477Sγ (grey).
