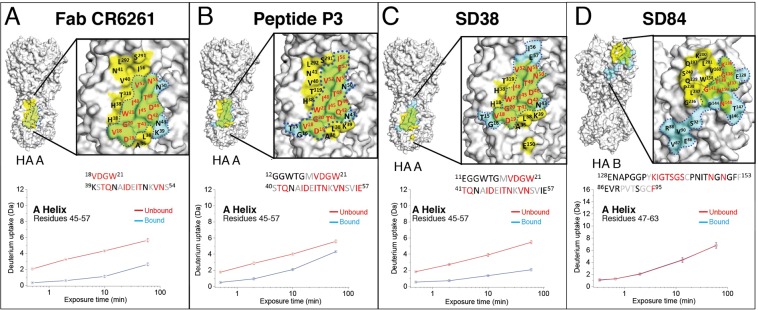
Figure 4.
HDX-MS accurately determines the epitope for each drug molecule and reveals distinct effects on the conformational dynamics of HA. The epitopes identified by HDX-MS for (A) Fab CR6261, (B) Cyclic Peptide P3, (C) Llama single domain SD38 and (D) Llama single domain SD84 are mapped onto the molecular surface representation of the corresponding HA strain. For each drug candidate, the areas identified as protected by HDX-MS were plotted in blue, and the residues shown to mediate contacts by X-Ray crystallography were mapped in yellow. Thus, the green area is the overlap between the epitopes identified by X Ray co-crystallography and HDX-MS, revealing that these methods generate similar results in all cases. The close-up view shows all amino acids identified as part of the epitope by X-Ray crystallography and HDX-MS with the residues identified by both methods highlighted in red. The PDB identifiers for the X-Ray co-crystal structures of the different drug candidates in complex with different HA strains are 3GBN (Fab-CR6261-HA A/Brevig Mission/1/1919), 5W6I (P3-HA A/Puerto Rico/8/1934), 6FYT (SD38 –HA A/Salamon Islands/3/2006) and 6CNV (SD84 –HA B/Brisbane/2008/60), respectively. The precise amino-acid sequences identified as the epitope by HDX-MS are also shown with residues identified by X-Ray crystallography colored in red, while those buried within the protein structure and therefore not accessible from the protein surface are shown in grey. Below, the deuterium uptake graphs of peptides originating from the A Helix are shown for the corresponding drug candidate. Peptides stemming from the A Helix in HA A/California//07/2009 strain (HA2 residues 45–57, Panels A–C) and the HA B/Brisbane/2008/60 strain (HA2 residues 47–63, Panel D) are essentially indistinguishable, demonstrating conservation of the unique conformational dynamics of the A Helix across distantly related HA subtypes. The deuterium incorporation graphs upon binding of each drug candidate show that the 3 broadly neutralizing HA stem binding drug candidates (Fab CR6261, P3 and SD38) significantly inhibit conformational breathing of the A Helix, whereas the strain specific HA head-binder SD84 does not. Furthermore, the deuterium incorporation rates of each drug candidate are distinct and reveal significantly larger protection upon binding of Fab CR6261 and SD38 than P3.