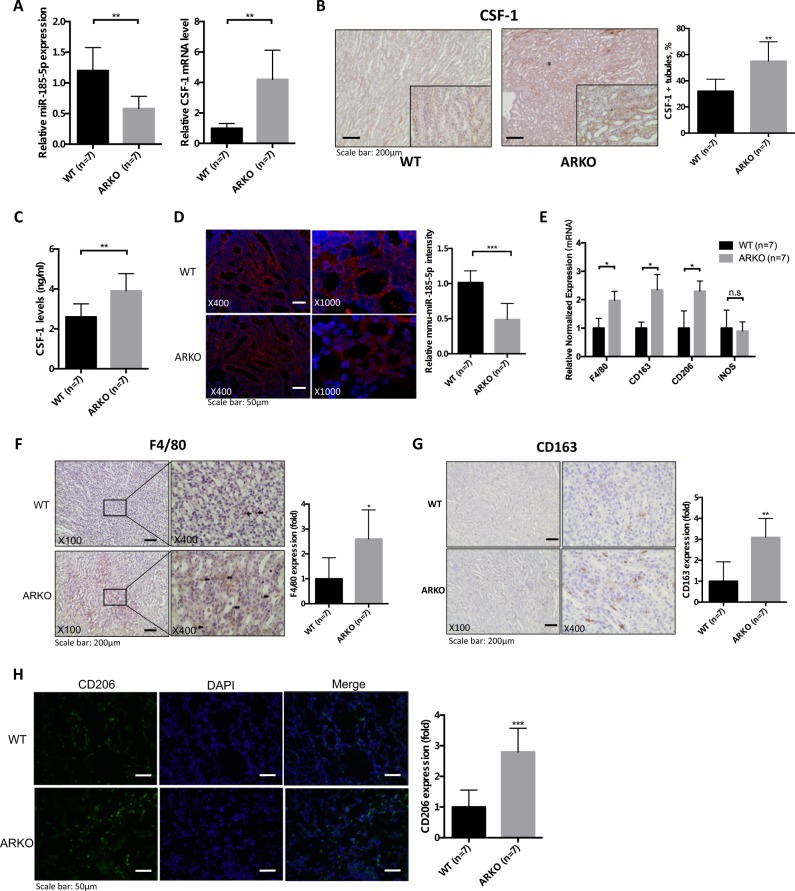
Fig. 6. Loss of androgen receptor (AR) increased renal CSF-1 expression and M2 macrophage infiltration in glyoxylate-induced intrarenal calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals deposition mouse model.
a The quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of CSF-1 gene and miR-185-5p expression in mice kidneys. b (IHC staining of mouse kidney tissues showing that loss of AR in Cdh16-ARKO mice increased the CSF-1 expression. Quantification of CSF-1 positive renal tubules is shown in the right panel. c Kidney CSF-1 levels in WT and Cdh16-ARKO mice. CSF-1 levels in kidney homogenates determined by ELISA. d Representative MISH staining results for mmu-miR-185-5p in kidney tissues from WT or Cdh16-ARKO mice. e AR deletion in the renal tubule led to increased mRNA levels of markers of pan-MΦs and M2-like MΦs, including F4/80, CD163, CD206 (mannose receptor), but not INOS, in kidneys from mice with glyoxylate injection for 6 days. f Immunostaining indicated increased renal F4/80-positive MΦs in the renal corticomedullary junction from Cdh16-ARKO mice at 6 days after glyoxylate injection. g Immunostaining indicated increased renal CD163-positive MΦs in the renal corticomedullary junction from Cdh16-ARKO mice at 6 days after glyoxylate injection. h Immunofluorescence indicated increased renal CD206-positive MΦs in the Cdh16-ARKO mice at 6 days after glyoxylate injection. For B, D, F, G and H, quantitations are at the right and all quantitations are mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. not significant compared with WT mice group