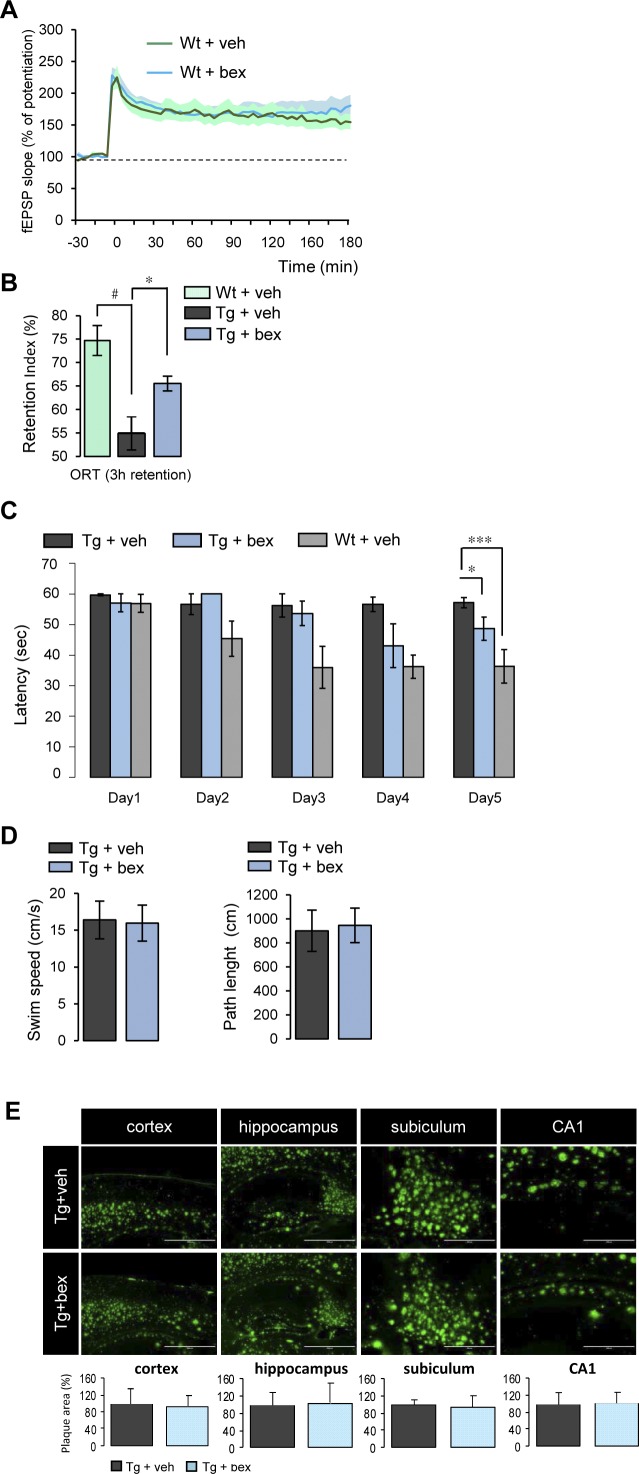
Figure S1. RXR activation improves cognition in an AD mouse model, independently of brain amyloid plaque load.
(A) 9–10-mo-old wild-type (Wt) mice treated with bexarotene (bex) (100 mg/kg/d) or vehicle (veh) by gavage (12 d). CA1 LTP in hippocampal slices of Wt male + bex (n = 4) was compared with Wt + veh (n = 4). P > 0.05, t test. (B) 9–10-mo-old 5xFAD transgenic (Tg) and wild-type (Wt) mice treated with bexarotene (bex) (100 mg/kg/d) or vehicle (veh) by gavage. Cognition in Tg + veh (n = 7) and Wt + veh (n = 5) mice was measured in the object recognition task (ORT). Bex treatment increased OR memory in Tg mice (Tg + bex, n = 8). Recognition memory is expressed as exploratory preference in retention test, 3 h post-training (compared with Wt + veh: #P < 0.05; compared with Tg + veh: *P < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison posttest). (C) Cognitive performance in Tg mice in Morris water maze (MWM) test was improved by a 10-d treatment with bex (training started following 5 d of treatment). Latency to reach the escape platform decreased on the fifth day of training in Wt and Tg mice treated with bex (n = 5 in each group; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 by ANOVA analysis followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison posttest, one-sided P values are presented for MWM experiments only). (D) Swim speed and path length measured in MWM test in Tg treated with bex or veh for 10 d (n = 5 in each group). (E) Amyloid plaque load measured on brain sections stained with anti-Aβ antibody in the cortex, hippocampus, subiculum, and hippocampal CA1 region. Results are expressed as percentage of Tg + veh (n = 5 for each condition; P > 0.05, t test). Data information: data are presented as mean ± SEM.