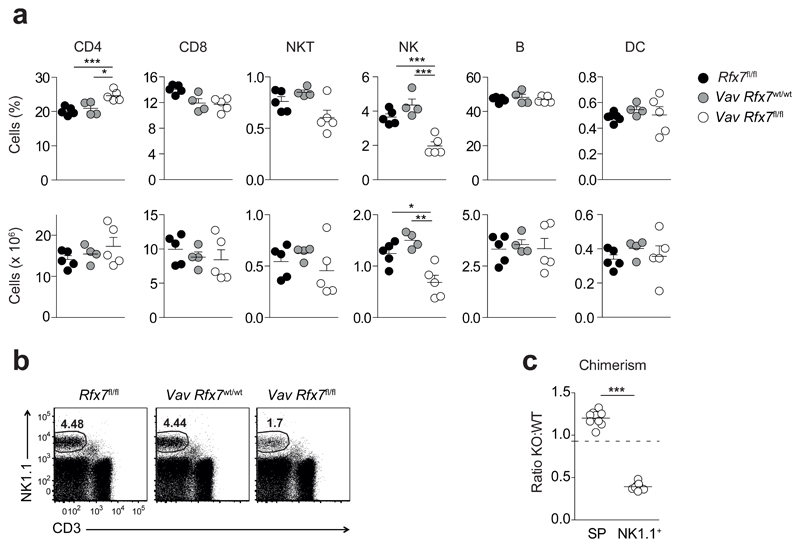
Figure 2. NK cells are strongly reduced in Vav Rfx7fl/fl mice.
(a) Percentages and absolute numbers of splenic CD4+ T cells (gated as CD3+CD4+), CD8+ T cells (gated as CD3+CD8+), NKT cells (gated as NK1.1+CD3+), NK cells (gated as NK1.1+CD3−), B cells (gated as CD19+), and conventional dendritic cells (DC; gated as CD11chiCD11bint-hi) from the indicated mice are shown. (b) A representative flow cytometric plot of NK cells in the spleen of Rfx7fl/fl, Vav Rfx7wt/wt, and Vav Rfx7fl/fl mice is shown (gated on lymphocytes). (c) The graph depicts the ratio of Vav Rfx7fl/fl (KO) over Vav Rfx7wt/wt (WT) for total splenocytes (SP) and NK cells (NK1.1+) in the spleen of Vav Rfx7wt/wt:Vav Rfx7fl/fl mixed BM chimeras. The dotted line represents the ratio of the injected mix. Results represent mean ± SEM of n=5 (Rfx7fl/fl), n=4 (Vav Rfx7wt/wt), and n=5 (Vav Rfx7fl/fl) mice (a) and n=9 mice per group (c), and are representative of at least three (a-c) independent experiments. Statistical comparison between the experimental condition lacking Rfx7 and controls were performed (a,c); *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001; Student’s t-test.