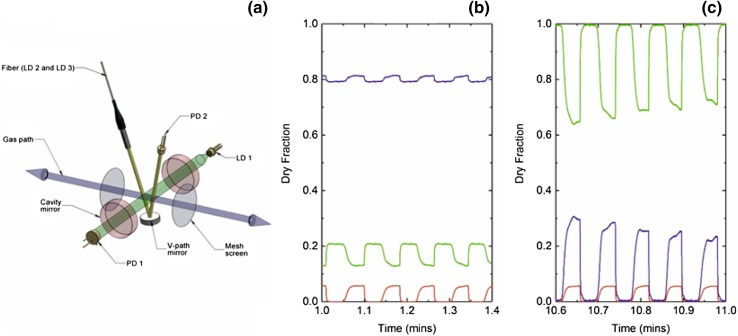
Fig. 2.
a Schematic of the multichannel absorption spectrometer and pneumotachograph within the MFS measurement head. The bi-directional gas path (blue) is shown along with the two mesh screens (gray), across which pressure drop is measured. Radiation used for probing O2 is injected into an optical cavity constructed from a pair of highly reflective mirrors (red) and collected by a photodiode (PD 1) positioned along the optical axis (green). Radiation probing CO2 and H2O vapor is launched into the v-path (yellow), reflected by a concave mirror, and collected by the photodiode (PD 2). The physical length of the optical cavity is commensurate with the diameter of a standard medical ventilation tube. b, c Dry gas fractions of N2 (purple), O2 (green), and CO2 (red) measured in real time (every 10 ms) as a participant breathes through the measurement head. The dry fraction of N2 is determined by the subtracting the dry fractions of O2 and CO2 from unity. b Data from an air breathing phase. c Data from the early stage of a nitrogen washout procedure