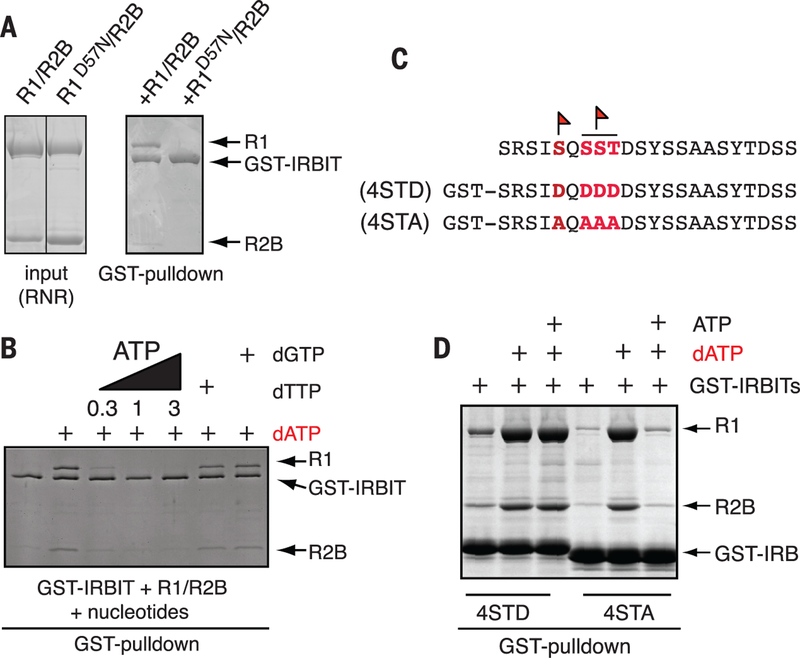
Fig. 2. IRBIT binds RNR when dATP is in the A-site and requires phosphorylation for its full binding activity.
(A) dATP occupancy of RNR’s A-site is required for IRBIT binding. GST-IRBIT was mixed with either R1/R2B or R1D57N/R2B (input, left) and 10 mM dATP and retrieved by glutathione-Sepharose (right). (B) IRBIT-RNR interaction is sensitive to ATP competition but insensitive to S-site occupancy. GST-IRBIT was mixed with R1/R2B and 3 mM dATP followed by addition of 0.3 mM ATP, 1 mM ATP, 3 mM ATP, 1 mM dTTP, or 1 mM dGTP. (C) Endogenous phosphorylation sites that were mapped on IRBIT (flags) and corresponding recombinant phosphomimetic or nonphosphorylatable mutants. (D) IRBIT phosphorylation prevents dissociation of the IRBIT-R1-dATP complex by ATP. GST-IRBIT4STD (STD) or GST-IRBIT4STA (STA) was mixed with R1/R2B and 3 mM dATP followed by addition of 1 mM ATP. In all panels, complexes were analyzed as in Fig. 1B.