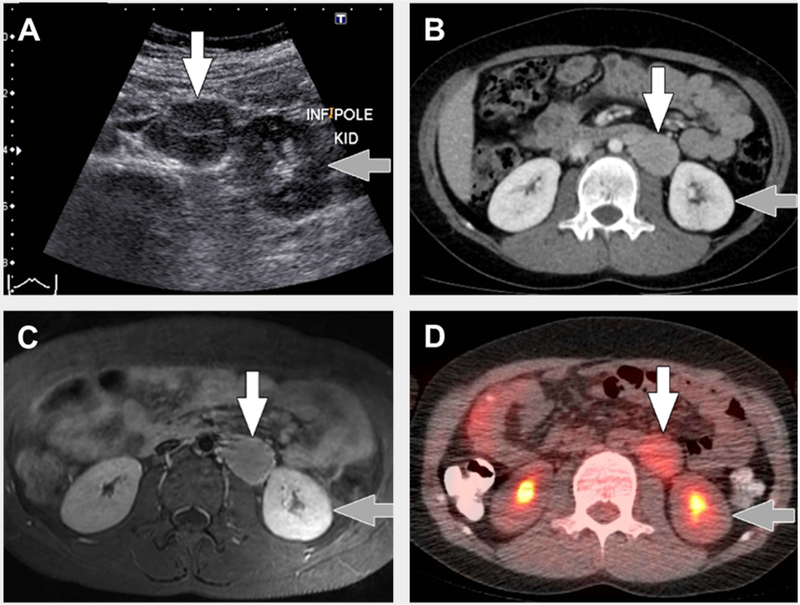
FIGURE 2. Typical imaging findings in unicentric Castleman disease.
8 year old with unicentric Castleman disease. (A) Transverse greyscale ultrasound image shows a hypoechoic mass (white arrow) in the left retroperitoneum near the lower pole of the left kidney (grey arrow). (B) Axial computed tomography (CT) with intravenous contrast only shows the mass (white arrow) adjacent to the lower pole of the left kidney (grey arrow) to be homogenously hyperenhancing relative to muscle. (C) Transverse T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with intravenous gadolinium-based contrast material shows the mass (white arrow) adjacent to the lower pole of the left kidney (grey arrow) to be homogenously hyperenhancing relative to muscle. (D) Axial fused 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG)/CT image shows uniform FDG uptake, SUVmax=3, in the mass (white arrow) adjacent to the lower pole of the left kidney (grey arrow).