Fig. 4.
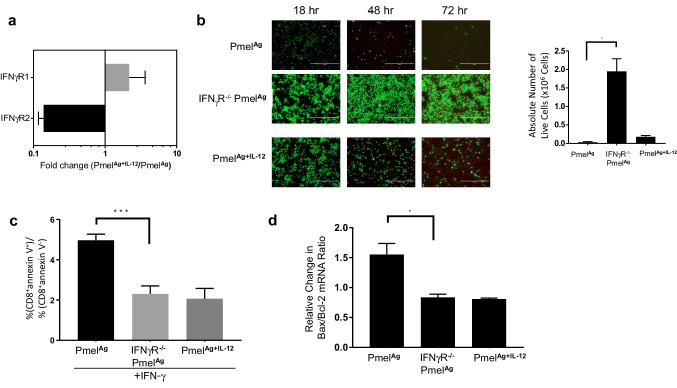
Lack of IFN-γ sensitivity protects activated CD8 + T cells from IFN-γ-induced apoptosis. a Adoptively transferred Thy1.1+ Pmel cells were sorted from cell suspensions prepared from similar size tumors (n = 3) 5 days after treatment with PmelAg or PmelAg+IL-12 cells, and analyzed for IFNγR1 and IFNγR2 expression by qPCR. Data are expressed as fold expression of PmelAg+IL-12 over PmelAg ±SD (p = 0.07). 1 × 106 ex vivo expanded wild-type PmelAg or PmelAg+IL-12, and IFNγR−/− PmelAg cell were recultured in fresh media. b Cell viability was determined after 24, 48, and 72 h of culture using the LIVE/DEAD® assay. c Apoptosis was measured by annexin V stain 24 h after culture. Data are presented as the average ratio of CD8+ annexin V+ over CD8+ annexin V− cells ± SD (n = 3). d RNA isolated from cells after 24 h of culture was analyzed by qPCR for expression of Bcl-2 and Bax. These values were used to calculate Bax/Bcl-2 ratio which directly associates with apoptosis [20]. Data are presented as the average change in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio relative to their respective baseline measurement ± SD (n = 3). Two-tailed Student’s t test was used, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, and ***p < 0.0001. Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments