Figure 1:
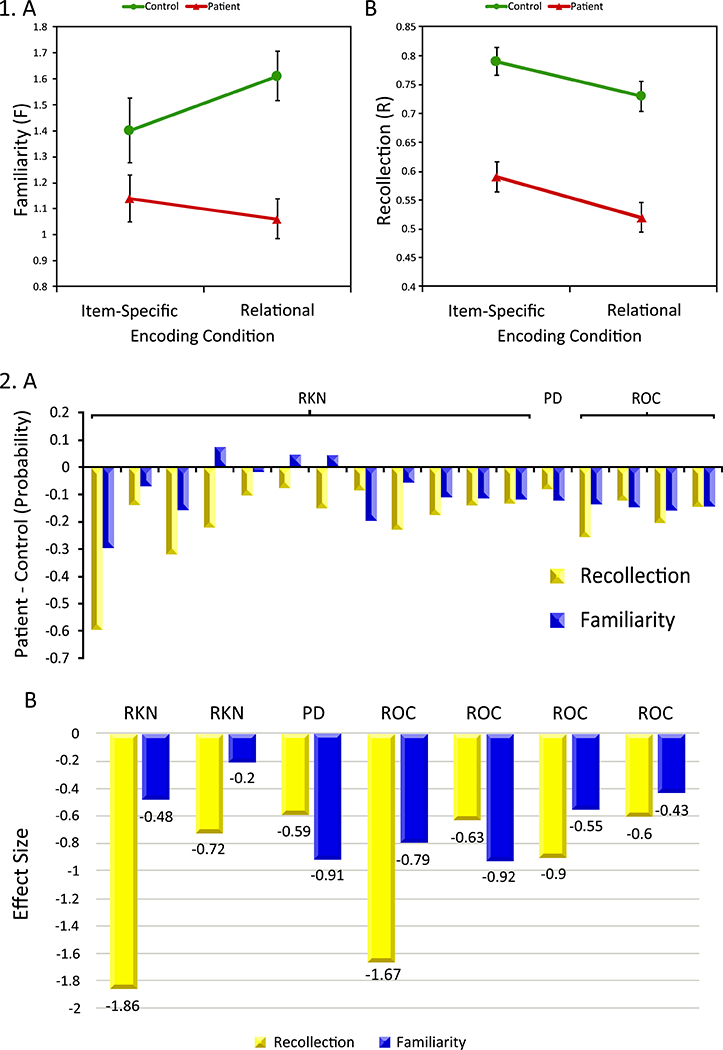
Panel 1, Mean (±SEM) familiarity and recollection in healthy controls (blue circles) and Sz patients (red triangles). (A) Familiarity reveals a group by encoding interaction, with more severe patient deficits following relational versus item-specific encoding, (B) Recollection reveals a main effect of group across both encoding conditions, with lower patient versus control performance. See Ragland, Ranganath 28 for additional results. Panel 2, Meta-analysis of recollection and familiarity deficits across 19 previous studies utilizing remember/know/new (RKN), receiver-operator characteristic (ROC), or process dissociation (PD) methods. (A) Recollection and familiarity estimates were recalculated with three probabilities models from three types of studies respectively, showing more impaired recollection in Sz patients than controls across studies. (B) Effect sizes of Sz on recollection were slightly larger than on familiarity. See 31 for study references.
