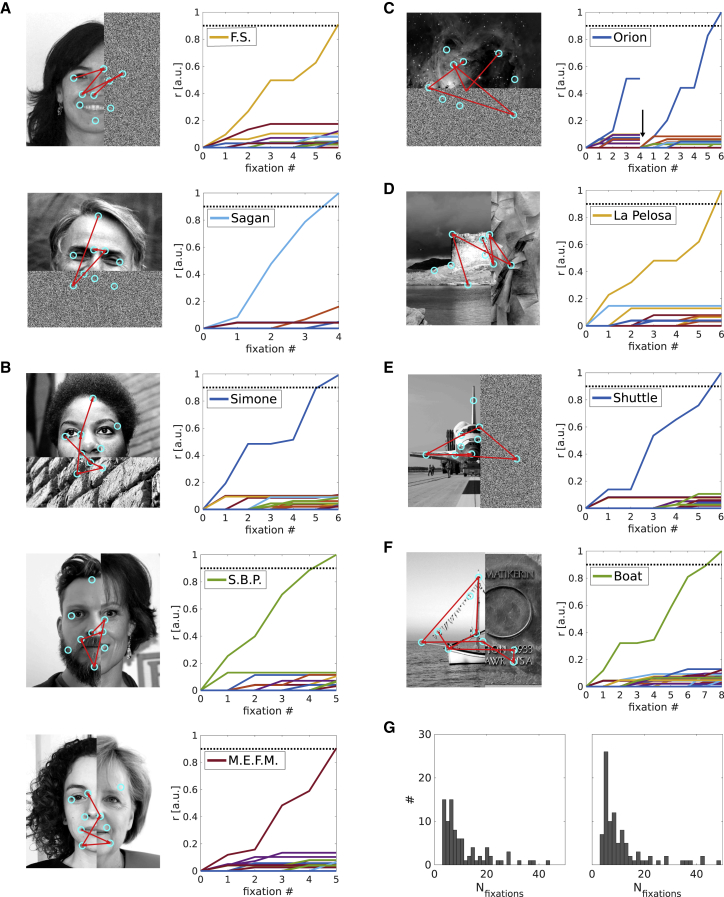
Figure 4.
Occlusions
The (expected) locations of occluded features can still serve as start and end points of saccades, however, occluded features rarely increment the output of the associated identity cells (stair patterns in line plots).
(A) Face stimuli with white noise occlusions. Saccades sequences (red arrows) superimposed on face stimuli (left). Cyan circles indicate the centers of all encoded local features. With each sampled feature, a firing rate of the corresponding identity cell is incremented (right).
(B) Same as (A) with real-world occlusions.
(C and D) Scene stimuli with white noise (C) and real-world (D) occlusions.
(E and F) Object stimuli with white noise (E) and real-world (F) occlusions.
(G) The total number of fixations (including resets) for white noise (left) and real-world occlusions.
Image credit: F.S., S.B.P., M.E.F.M.: used with permission; Boat, La Pelosa Beach: supplied by author, with permission; Shuttle: public domain image; Carl Sagan, Nina Simone, Orion, Sigourney Weaver, Angela Merkel, brick wall, Picasso, Emmy Noether plaque: Creative Commons Attribution.