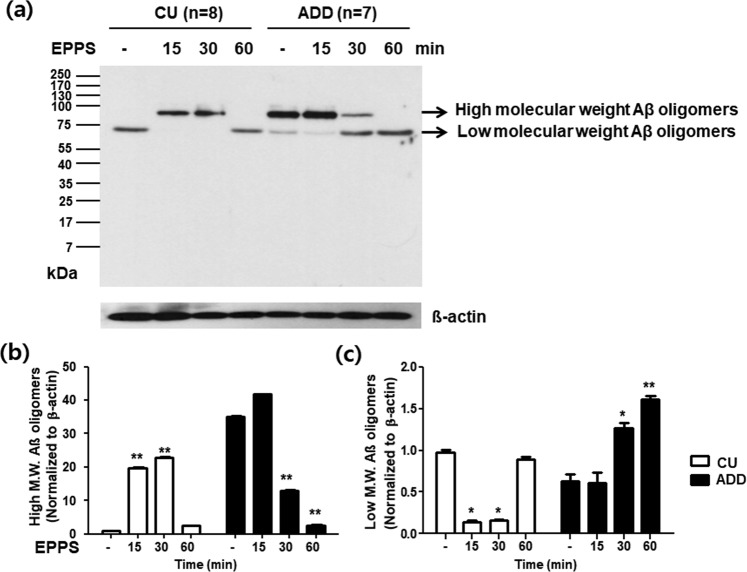
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of nasal secretions in 7 patients with Alzheimer’s disease dementia (ADD) and 8 cognitively unimpaired (CU) individuals. Western blots using 6E10 antibody were performed for nasal secretions of 7 ADD patients with amyloid deposition on PET and 8 CU individuals without amyloid deposition on PET. (a) Western blotting of nasal secretions of the ADD patients and CU individuals at baseline, and 15, 30 and 60 min after 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinepropanesulfonic acid (EPPS) treatment. It presents that the baseline nasal secretion of ADD patients contains larger amount of high molecular weight amyloid β (Aβ) oligomers of ~90 kDa compared to the CU individuals and less other molecular weight Aβ oligomers (lane 1, 5), and by treating EPPS for 60 min, high molecular weight Aβ oligomers were gradually disassembled to lower molecular weight Aβ oligomers under 70 kDa. After 60 min, a band at ~90 kDa completely disappeared and a band at ~70 kDa definitely emerged (lane 6–8). (b) The amount of high molecular weight Aβ oligomers gradually decreases until 60 min in the nasal sample of ADD patients. The amount of high molecular weight Aβ oligomers in the ADD group was significantly lower at 30 min and 60 min than at baseline. (c) The amount of disassembled lower molecular weight Aβ oligomers gradually increases until 60 min in the nasal sample of ADD patients. The amount of disassembled lower molecular weight Aβ oligomers in the ADD group was significantly higher at 30 min and 60 min than at baseline. Data are mean (SEM). *p < 0.005 vs. baseline and **p < 0.001 vs. baseline by Bonferroni post hoc analysis.