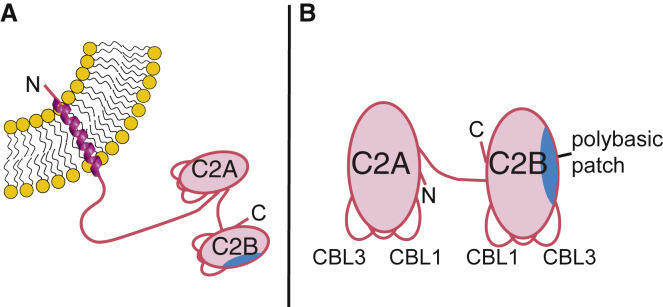
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of synaptotagmin. (A) Full-length synaptotagmins contain an N-terminal transmembrane helix anchored to either the secretory vesicle or plasma membrane (65, 66) and two C-terminal C2 domains. (B) The Syt-1 and Syt-7 C2AB protein fragments used in this study consist of the C-terminal C2 domains, which coordinate Ca2+ ions and insert into membranes primarily via Ca2+-binding loops (CBL1 and CBL3). The C2B domains additionally contain a polybasic patch (blue shading) that can interact with anionic lipids in a Ca2+-independent manner. To see this figure in color, go online.