Fig. 1.
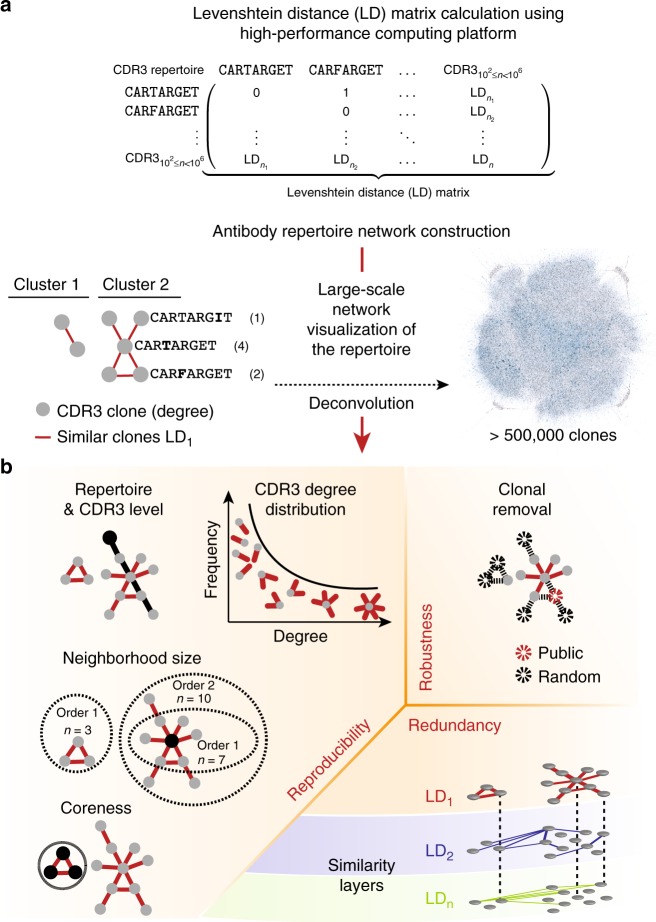
Large-scale network analysis reveals the architecture of antibody repertoires and its three fundamental principles. a Large-scale networks (>500,000 nodes) of antibody repertoires were constructed from the Levenshtein distance (LD, edit string distance) matrix of CDR3 clonal sequences (a.a) using a custom high-performance computing platform (see Methods). Networks represent antibody repertoires of similar CDR3 nodes connected by edges when amino acid CDR3 sequences differ by a predetermined LD. All clones of a repertoire connected at a given LD form a similarity layer (LDn). b Deconvolution of the complexity of antibody repertoire architecture was performed by quantifying (i) its reproducibility through global and clonal (local) properties or features, (ii) robustness to clonal removal and (iii) redundancy across its similarity layers in the sequence space (Supplementary Fig. 1)