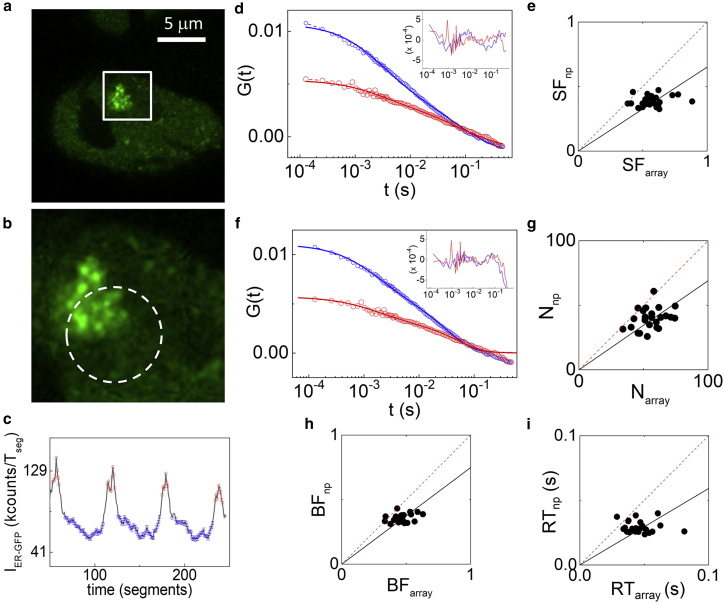
Figure 5.
Measurement of the mobility of the estrogen receptor (ER) inside and outside an engineered prolactin gene array. (a and b) The measurements were performed orbiting across the prolactin gene array. (c) The intensity of the GFP-ER signal is used as a reference for sorting the ACFs corresponding to the array (red) and to the nucleoplasm (blue). (d and e) Analysis with a two-diffusion component model is shown. (d) A global fit performed on the sorted ACFs (red: sorted ACF of the array, blue: sorted ACF of the nucleoplasm) yields a shared value of diffusion coefficients Dslow = 0.07 μm2/s for the slow-diffusing population and Dfast = 2.1 μm2/s for the fast diffusing one. (e) Scatter plot of the SF was calculated in the two probed nuclear regions. The solid black line is a linear fit of the data with intercept fixed and with slope 0.65. (f–i) Analysis with the FM, showing the fitted ACFs (f) and the scatter plots of the number of proteins (g), the BF (h), and the RT (i) for the nucleoplasm and for the array, along with the corresponding linear fits ((g) slope = 0.69; (h) slope = 0.75; (i) slope = 0.59). Residuals are shown as plot insets in (d and f). To see this figure in color, go online.