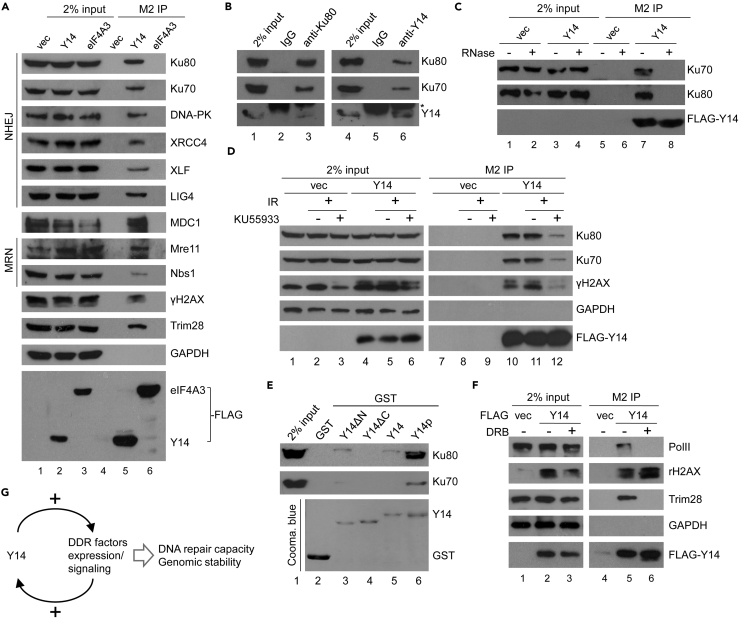
Figure 3.
Y14 Interacts with DNA Damage Repair Factors
(A) HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (vec) or vector encoding FLAG-Y14 or FLAG-eIF4A3. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG, followed by immunoblotting using antibodies against FLAG or indicated proteins.
(B) HEK293 cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using control IgG or anti-Ku or anti-Y14, followed by immunoblotting. Asterisk indicates the immunoglobulin light chain.
(C) HEK293 cells were transfected with the empty or FLAG-Y14 vector. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG in the cell lysates in the absence (−) or presence (+) of RNase A, followed by immunoblotting.
(D) Transfected cells as in (C) were left untreated or were treated with the ATM inhibitor KU55933, followed by 10 Gy irradiation. The cell lysates were each subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG, followed by immunoblotting.
(E) In vitro pull-down assay was performed by incubating GST or GST-Y14 (full-length, ΔN, ΔC, or phosphorylated) with the HeLa cell lysate. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Ku70/80. GST fusions were detected by Coomassie blue staining.
(F) HEK293 cells were transfected with the empty (vec) or FLAG-Y14 vector. FLAG-Y14 transfectants were mock treated or treated with the RNA polymerase II inhibitor DRB. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblotting.
(G) Model shows the role of Y14 in a positive circuit of DDR signaling. Y14 promotes the expression of several DDR factors including ATM, which is likely required for Y14 function in DNA damage repair.